Figure 2.
Molecular Basis of Kinetochore Recruitment of CENP-OPQUR
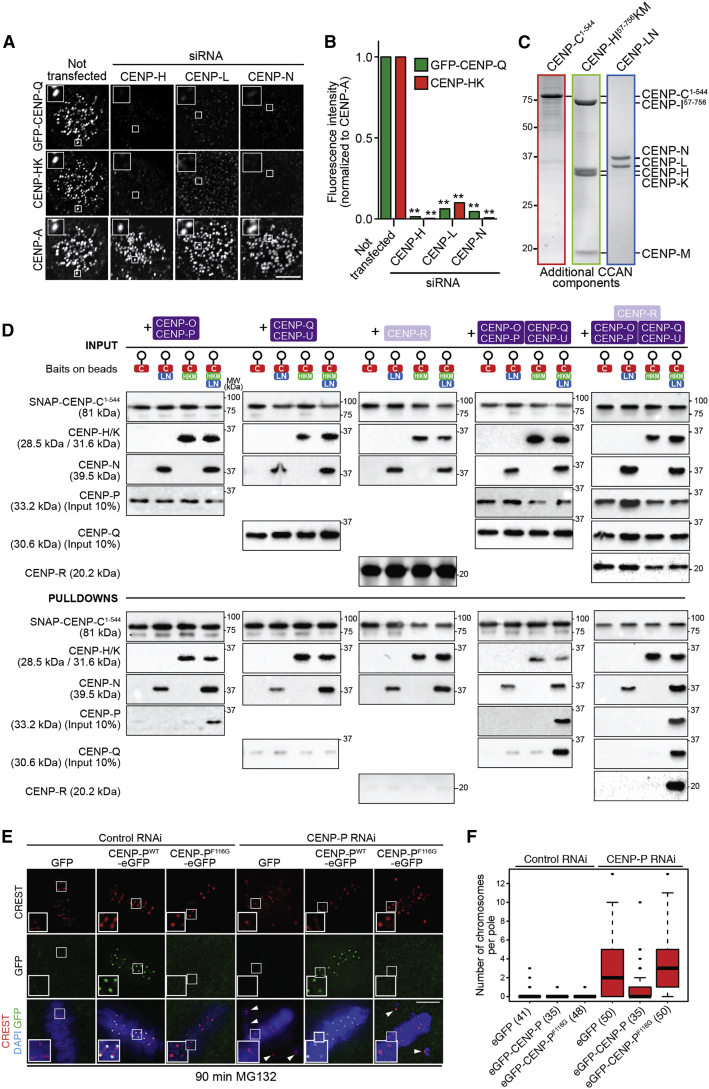
(A) Depletion of CENP-H, CENP-L, or CENP-N prevented kinetochore localization of GFP-CENP-Q in HeLa FlpIn TRex cell lines stably expressing GFP-CENP-Q, as shown by representative images. CENP-HK complex is also lost from kinetochores during the aforementioned RNAi depletions. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(B) Quantification of the amount of GFP-CENP-Q (green bars) and CENP-HK (red bars) at kinetochores following CENP-H, CENP-L, or CENP-N depletion. ∗∗p ≤ 0.01. Graph shows representative results from one of three independent experiments. A minimum of 158 kinetochores was quantified.
(C) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE of recombinant CENP-C1–544, CENP-HIΔ56KM, and CENP-LN used in (D).
(D) Pull-down assays using SNAP-CENP-C1–544 bait. CENP-OP binds the solid phase only in the presence of CENP-HIΔ56KM and CENP-LN. Subsequently, CENP-QU and CENP-R can also be recruited. Shown are Western blots of the indicated species. The experiment shown is representative of three technical replicas.
(E) RNAi-resistant GFP-CENP-P localized to the kinetochore after depletion of endogenous CENP-P, while GFP-CENP-PF116G did not. CREST signal (red) was unaffected by CENP-P depletion or by impaired localization of GFP-CENP-PF118G. DAPI (DNA) is shown in blue. Arrowheads indicate misaligned chromosomes. MG132 (10 μM) was added to prevent mitotic exit. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(F) Quantification of the experiment in (E). The number of cells analyzed is in parentheses. Error bars represent standard deviations. See also Figure S2 and Figure S3.