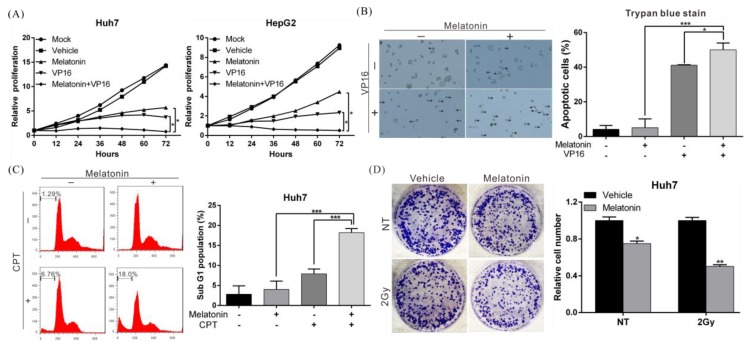
Figure 2.
Melatonin enhanced the sensitivity of HCC cells to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. (A) The proliferation capacity of Huh7 and HepG2 cells treated with 1 mM melatonin, 200 µM etoposide (VP16), or both was monitored using an xCELLigence real-time cell analyzer. p < 0.05 (*), as assessed using Student’s t-test. (B,C) An trypan blue exclusion assay and flow cytometry showed that combined treatment with 1 mM melatonin significantly increased the cytotoxicity of 200 µM etoposide (VP16) and 1 µM camptothecin (CPT) in Huh7 cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. The arrows indicate the apoptotic cells. (D) Effect of melatonin on the radiosensitivity of Huh7 cells. Cells were irradiated with Cs-137 at a dose of 2 Gy, followed by treated with/without 1 mM melatonin for 24 h and then cultured for an additional 10 days in the absence of melatonin (left panel). The numbers of foci were counted, and the results are presented in the right panel. p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***). All experiments were performed in triplicate.