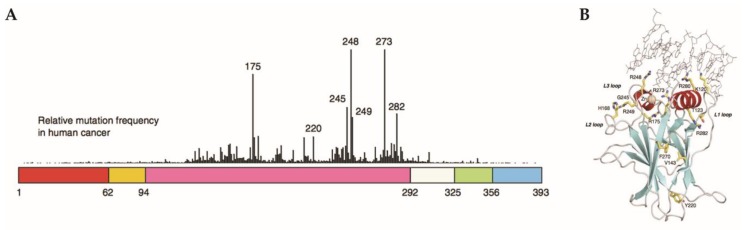
Figure 3.
Most TP53 mutations are in the DNA binding domain. (A) The schematic view of the domains of p53 protein. The protein has 393 residues with numerous different domains including the N-terminus (red), proline rich domain (orange), DNA binding domain (purple), tetramerization domain (green) and negative regulatory domain/C-terminus (blue). The peaks represent the frequency of mutations in cancer with the DNA binding domain containing the six hot spot mutations. (B) Ribbon diagram of DNA-bound p53 (PBD ID 2AHI). The residues highlighted in yellow represent residues that are hot spot mutations as well as other residues of interest. Modified and reprinted with permission from Springer Nature: [Springer Nature] [Oncogene] [112].