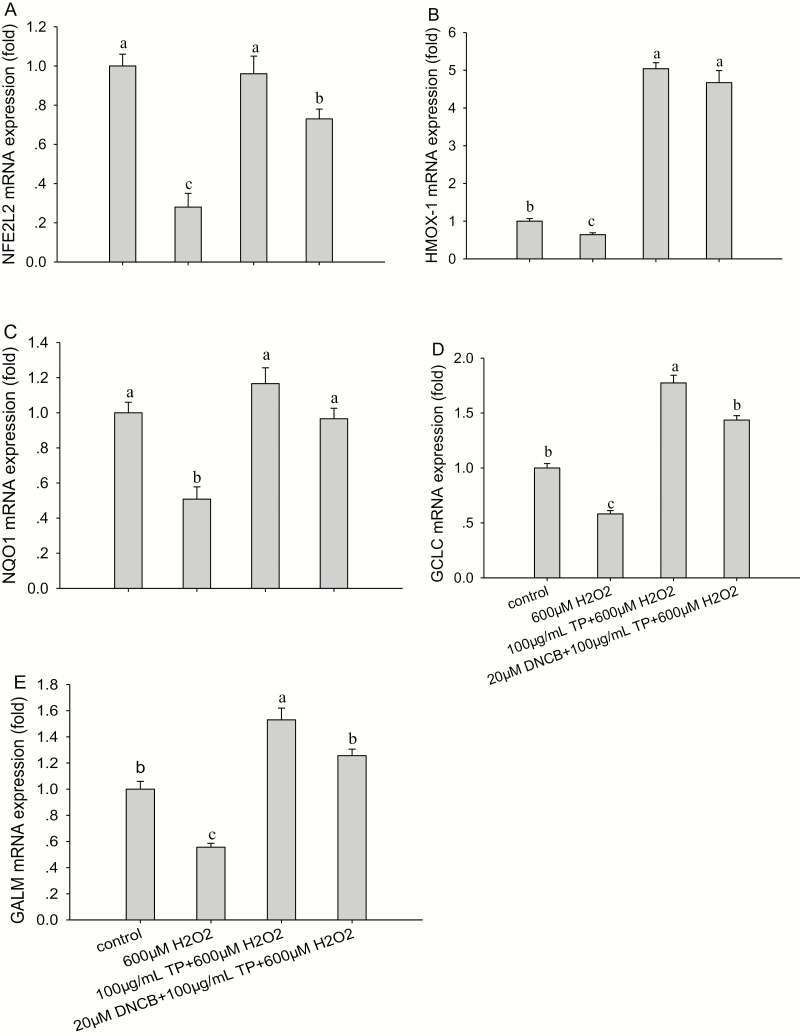
Figure 6.
Effect of tea polyphenol (TP) treatment on mRNA abundance of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2) signaling pathway proteins in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMEC) under control and oxidative stress (OS) conditions. (A to E) mRNA abundance of NFE2L2, heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX-1), NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), and glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit (GCLM) in BMEC under control and OS conditions. The BMEC were preincubated with a MAPK-specific inhibitor, 2,4-dinitrochloro-benzene (DNCB), for 30 min and then treated with or without TP (100 µg/mL) for another 12 h followed by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2; 600 µM) exposure for 6 h. The mRNA abundance of NFE2L2, HMOX-1, NQO1, GCLC, and GCLM was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Means with different superscript letters differ (P < 0.05). There were 5 replications for each experiment and each well.