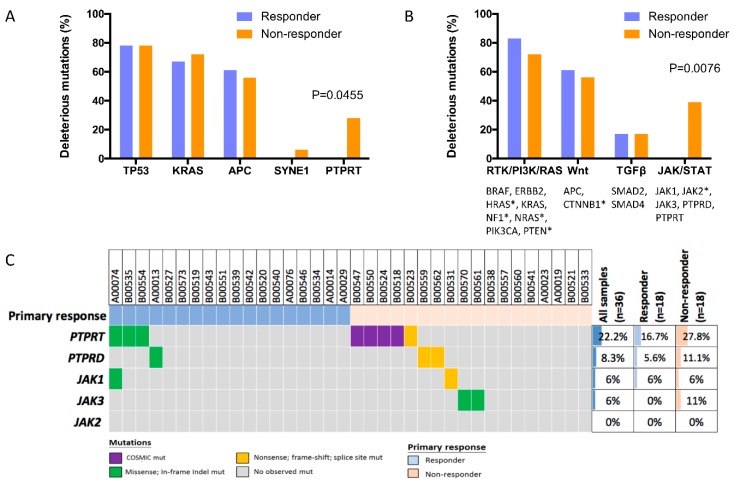
Figure 2.
Mutations in PTPRT/PTPRD, genes of the JAK/STAT pathway, discriminate between bevacizumab responders and non-responders. Postulated deleterious mutations in single genes with high mutation frequencies in our cohort (A) and in multiple genes involved in important colorectal cancer (CRC) signaling pathways (B) were evaluated for bevacizumab responders and non-responders. Genes included in the pathway-based analysis are listed, and genes without any detected mutations in our cohort are indicated by a star. Postulated deleterious variants were variants with existing COSMIC ID or—if the analyzed genes were tumor suppressor genes—truncating variants. In our analysis, genes with detected mutations that were considered as tumor suppressors were APC, PTPRD, PTPRT, SMAD2, SMAD4, SYNE1, and TP53. The proportion of responders and non-responders harboring such variants is depicted. Statistical analysis was performed with the Fisher’s exact test. An oncoprint of genes involved in JAK/STAT signaling is shown (C).