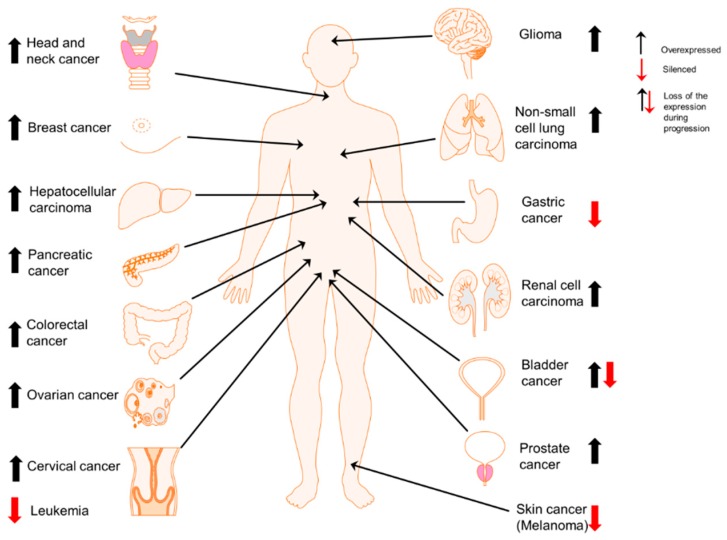
Figure 1.
Cell type-dependent expression of Prx II in cancers. Overexpression of Prx II in majority of cancer types including head and neck [25], breast [35], liver (hepatocellular carcinoma) [22], pancreatic [36], colorectal [12], ovarian [37], cervical [38], brain (glioma) [39], lung (non-small cell lung cancer) [21], kidney (renal cell carcinoma) [40] and prostate cancers [20] and epigenetically silenced expression of Prx II in gastric cancer [24], melanoma [41] and leukemia [5]. Specially, in bladder cancers, overexpressed Prx II is significantly reduced with the cancer progression [42].