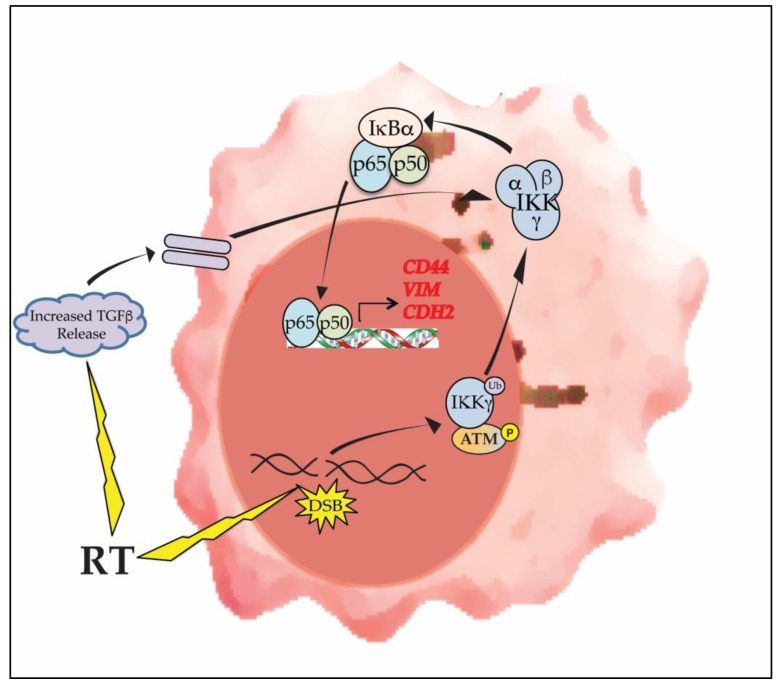
Figure 4.
RT promotes mesenchymal change in GBM via activation of NF-κB. DNA damaging therapies such as RT induce NF-κB activation by forming DNA DSBs. This ‘atypical’ activation pathway involves phosphorylated ATM and mono-ubiquitinated IKKγ (NEMO). RT also induces the release of microenvironmental factors such as TGFβ that cooperate with NF-κB in promoting expression of mesenchymal proteins.