Fig. 4.
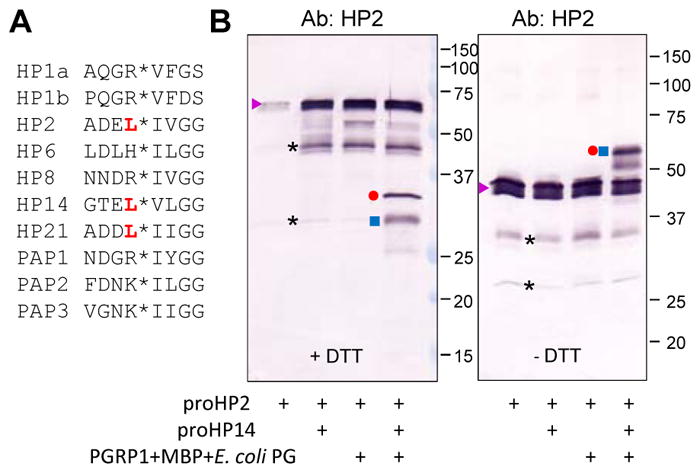
Limited proteolysis of the recombinant proHP2 by auto-activated HP14. (A) Comparison of amino acid sequences near the cleavage activation sites (*) of the known protease components in the M. sexta proPO activation system. The preceding Leu residue in HP2, HP14, and HP21 is red, bold font. (B) Purified proHP2 (200 ng/μl, 1 μl) was reacted with proHP14 (100 ng/μl, 1 μl) only, a mixture of E. coli PG (1 μg/μl, 1 μl), MBP (400 ng/μl, 1 μl), PGRP1 (400 ng/μl, 1 μl) and 15 μl buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM CaCl2, pH 7.5), or both at 37 °C for 2 h. The reaction mixtures were treated with SDS-sample buffer with (left panel) or without (right panel) DTT, separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and subjected to immunoblot analysis using 1:1000 diluted HP2 antiserum as the primary antibody. The major bands are proHP2 (▶), HP2 catalytic domain (●); HP2 clip domain and linker (■), cleaved yet attached HP2 (●■) under non-reducing conditions (i.e. no DTT), and uncharacterized (*).
