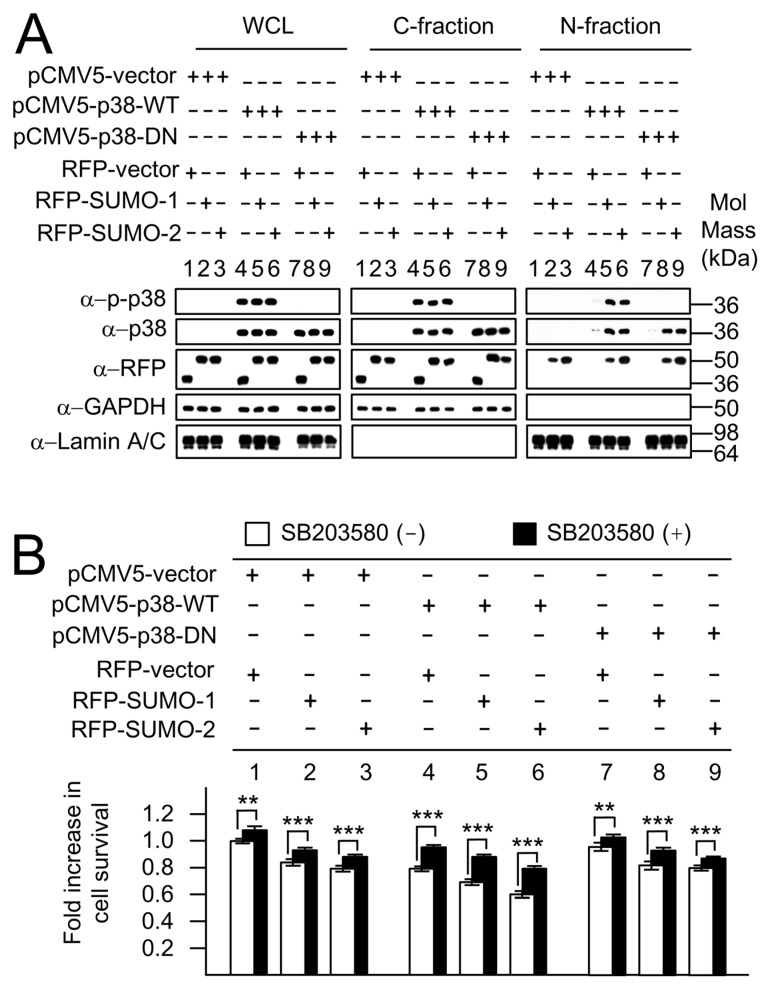
Figure 7.
SUMOs mediate the nuclear transport of p-p38, p38-WT and p38-DN. AGS cells co-transfected with p38 proteins (wild type pCMV5-p38-WT and dominant negative pCMV5-p38-DN), and RFP-SUMOs were characterized for nuclear transfer of p38 and for SUMO-mediated p38 apoptotic pathway during H. pylori infection. (A) p38-WT and p38-DN were blotted with anti-p-p38 and anti p38 antibodies. Other antibodies used have been described in Figure 3. p38-DN was detected only using anti-p38 antibody, and not when anti-p-p38 antibody was used. p38 and p-p38 proteins were clearly observed in the nuclear fraction only when co-transfected with RFP-SUMO-1 and RFP-SUMO-2, and not distinctly when cotransfected with RFP alone, demonstrating that the nuclear localization is dependent on SUMOs. This effect was found to be independent of p38 phosphorylation as the nuclear localization of the phosphorylation sites mutant p38-DN was also dependent on the presence of SUMOs; and (B) p38 inhibitor (SB203580) was used in the MTT assay to show the effects of the increased levels of p38 and SUMOs in the p38 pathway. Compared with the basal state, p38-WT enhanced apoptosis (i.e., decreased cell survival), whereas p38-DN had no such function during H. pylori infection, highlighting the importance of p-p38, and consistent with p38-DN being a non-activatable (non-phosphorylatable) p38. The Western blots (A) were repeated three times and representative images are shown. The MTT assays (B) were repeated four times and the results shown are the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t test. p < 0.05 was considered significant; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.