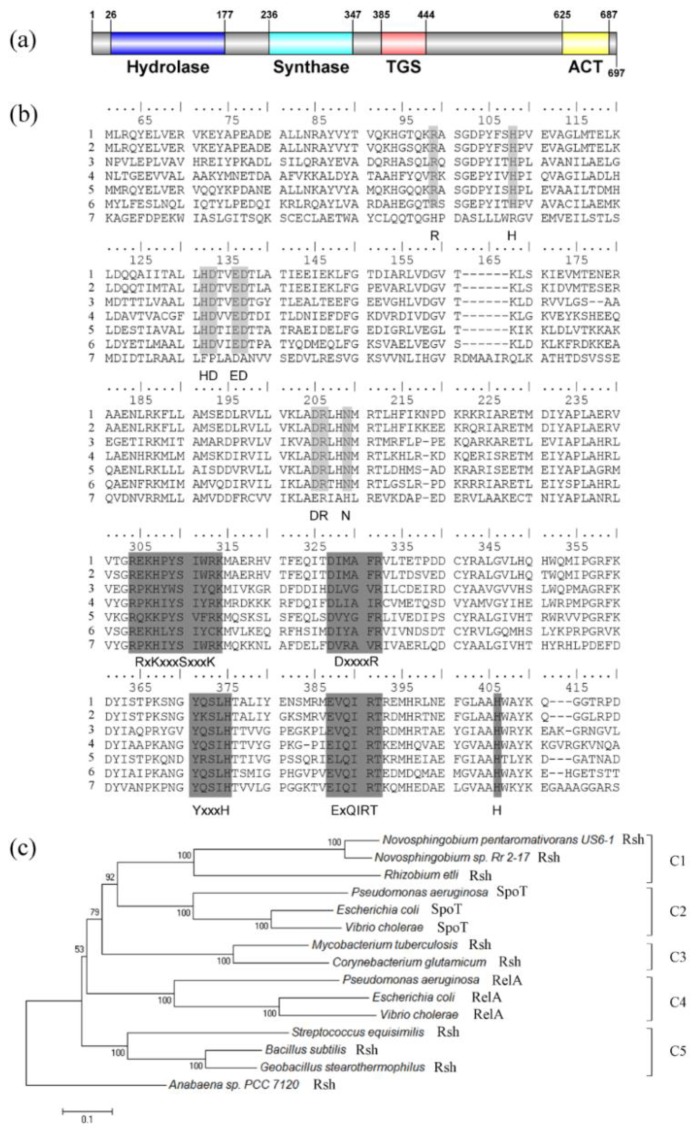
Figure 1.
Sequence analysis of RshUS6–1 protein. (a) RshUS6–1 domain; (b) amino acid alignment of RelA/SpoT homologs. Line 1: RshUS6–1. Line 2: RshRr2–17. Line 3: RshMtb. Line 4: RshSeq. Line 5: RshRet. Line 6: SpoTEcoli. Line 7: RelAEcoli (see in Materials and Methods). Light grey boxes represent six conserved motifs in HD domain (HD 1: R. HD 2: H. HD 3: HD. HD 4: ED. HD 5: DR. HD 6: N) while dark grey boxes represent five conserved motifs in Syn domain (Syn 1: RxKxxxSxxxK. Syn 2: DxxxxR. Syn 3: YxxxH. Syn 4: ExQIRT. Syn 5: H) [26]; (c) phylogenetic tree based on RelA/SpoT homologs. Sequences, available at NCBI GenBank, were aligned by using the ClustalW algorithm [27] in MEGA version 6.0 [28]. Then a phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method [29] with 1000 bootstrap replicates [30] after cutting off the redundant sequences at the end, with the use of MEGA version 6.0. The Rsh protein from Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 (accession number BAB77915) was used as outgroup [31]. There were five clusters: C1 for Rsh in Alphaproteobacteria, C2 for SpoT in Gammaproteobacteria, C3 for Rsh in Actinobacteria, C4 for RelA in Gammaproteobacteria, C5 for Rsh in Firmicutes.