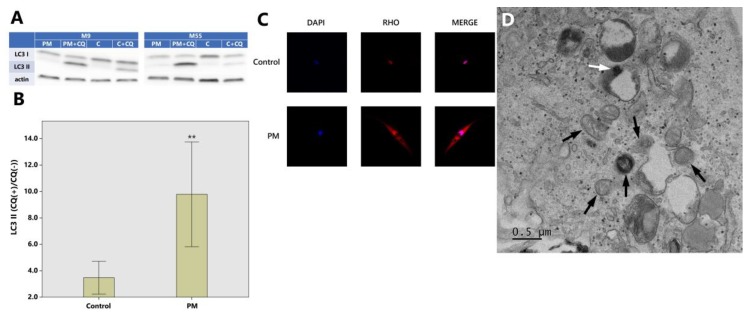
Figure 2.
Autophagic degradation is increased in dermal fibroblasts exposed to PM10. (A) Cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) and Western blotting; PM: particulate matter exposure, PM + CQ: particulate matter + chloroquine exposure, C: control (exposure to nothing), C + CQ: control + chloroquine; LC3: microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B (a central protein in the autophagy pathway). (B) The ratio of LC3-II with and without chloroquine which represent autophagic activity (flux) are 3.47 ± 1.96 (control) and 9.78 ± 6.24 (PM) (Western blot analysis) (** p < 0.01). (C) LC3 puncta monitored from fluorescence microscopy are increased in PM10 treated HDFs compared to control. Merged images were obtained with DAPI (4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) (nucleus; blue) and RHO (Alexa Fluor 594, Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) (LC3; red). The images were captured at 20× magnification. (D) TEM photo shows deformed mitochondrias (black arrows) and PM internalization in the autolysosome (white arrow) in PM-exposed HDF. As for Western blot analysis, the images are representative of three independent experiments on n = 8 sample pairs (PM, control). LC3-II expression is normalized to actin (arbitrary units). Data are provided as mean ± SD. The statistical significance of difference between control and experimental data for autophagy was analyzed using the paired t-test. p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis of data was performed using SPSS for Windows software (version 15.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).