Figure 1.
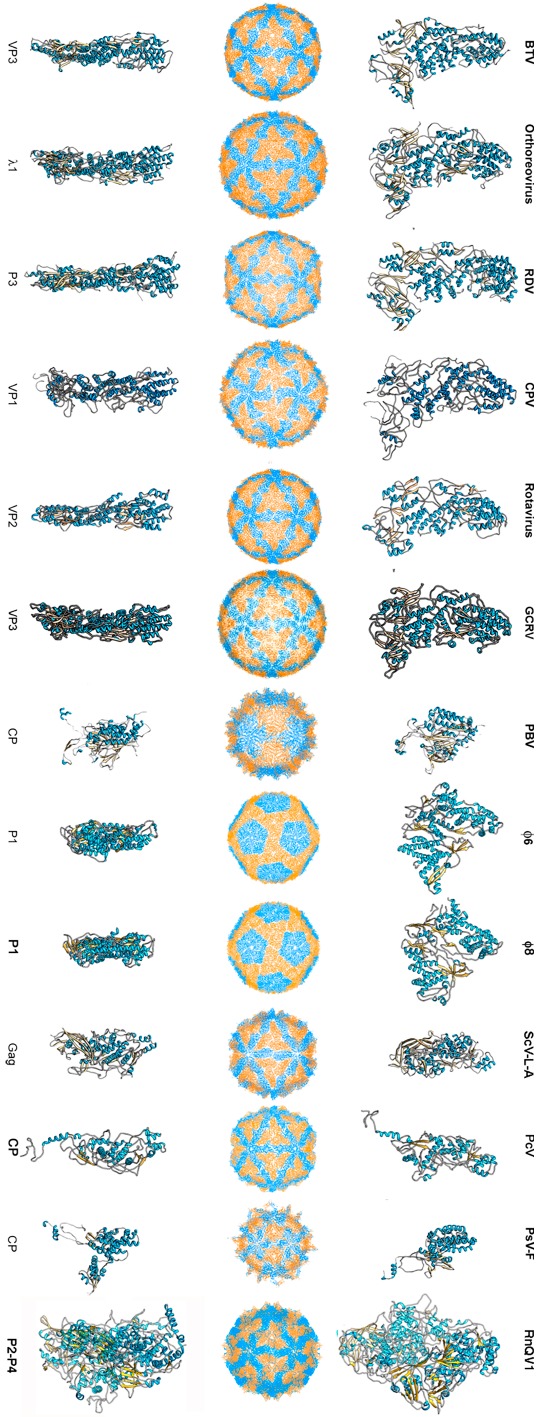
T = 1 capsid protein X-ray- and cryo-EM-based structures. Top row: T = 1 capsids of bluetongue virus (BTV), orthoreovirus, rice dwarf virus (RDV), cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (CPV), rotavirus, grass carp reovirus (GCRV), picobirnavirus (PBV), ϕ6 phage and ϕ8 phage, L-A virus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ScV-L-A), Penicillium chrysogenum virus (PcV), Penicillium stoloniferum virus F (PsV-F), and Rosellinia necatrix quadrivirus 1 (RnQV1), viewed along a two-fold axis of icosahedral symmetry (center row). BTV VP3 [2] (PDB accession number 2btv; 901 residues), λ1 [41] (1ej6; 1275 residues), P3 [42] (1uf2; 1019 residues), VP1 [19] (3cnf; 1333 residues), VP2 [43] (3kz4; 880 residues), GCRV VP3 [22] (3k1q; 1027 residues), PBV CP [23] (2vf1; 590 residues), ϕ6 P1 [44] (4btq; 769 residues) and ϕ8 P1 [45] (4btp; 792 residues), Gag [26] (1m1c; 680 residues), PcV CP domain A [46] (3j3i; 498 residues; complete CP 982 residues), PsV-F CP [29] (3es5; 420 residues) and RnQV1-W1118 P2 and P4 [36] (5nd1; 972 and 1005 residues, respectively), shown from top view. Bottom row: side views of the same structures (T = 1 shell exterior at right).
