Figure 1.
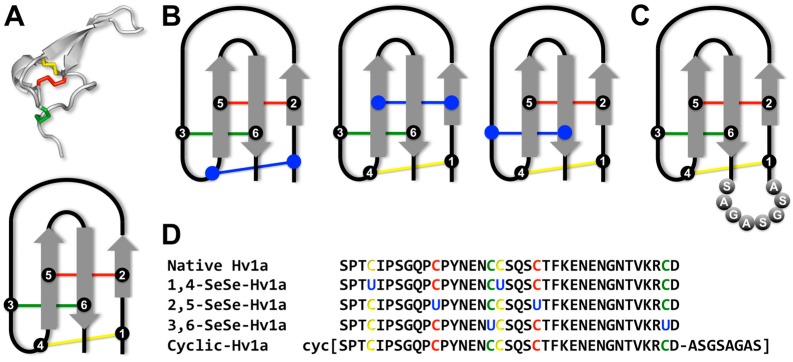
Sequence and structure of Hv1a and analogs with the colors indicating individual disulfide bonds (C1-C4 = yellow; C2-C5 = red and C3-C6 = green) (A) Top panel: Three-dimensional structure of native Hv1a (PDB 1AXH; [7]). Bottom panel: Schematic of the inhibitor cystine knot (ICK) motif of Hv1a, which comprises an antiparallel β-sheet (shown in grey) stabilized by a cystine knot. The six cysteine residues that form the cystine knot are labelled 1–6; (B) Schematic of the ICK motif for the three diselenide analogs of Hv1a. The blue color indicates replacement of a disulfide bond with a diselenide bond; (C) Schematic of the ICK motif for the cyclic Hv1a analog. The eight residues that form the linker bridging the N- and C-termini are labelled; (D) Amino acid sequences of native Hv1a and the various analogs used in this study.