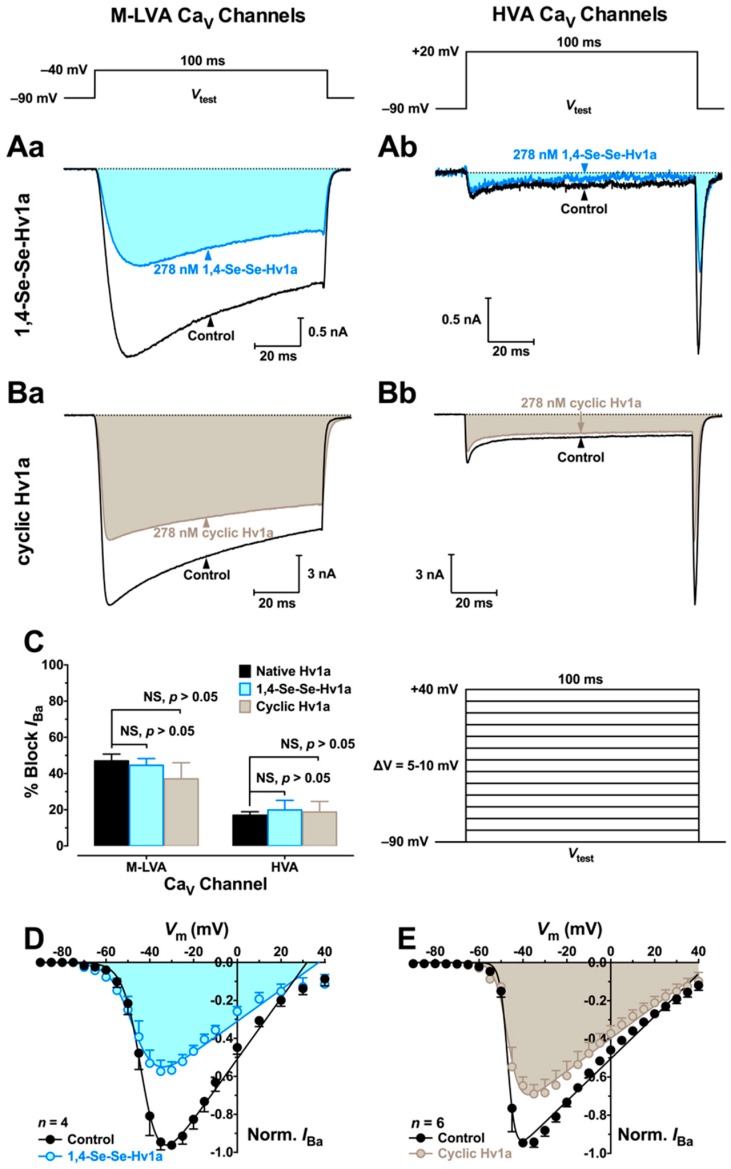
Figure 5.
Effect of Hv1a and analogs on CaV channels in cockroach dorsal unpaired median (DUM) neurons. (A,B) Typical effects of (A) 1,4-SeSe-Hv1a and (B) cyclic Hv1a on IBa. Representative control (black) and toxin (cyan and shaded for 1,4-Se-Se-Hv1a, grey and shaded for cyclic Hv1a) traces elicited by a 100-ms depolarising test pulse (Vtest) to −40 mV (left-hand ‘a’ panels; M-LVA CaV channel currents) or +20 mV (right-hand ‘b’ panels; HVA CaV channel currents). The dotted line represents zero current. Voltage protocols are shown above traces; (C) Comparison of average block of M-LVA and HVA IBa by native Hv1a (black), 1,4-SeSe-Hv1a (cyan), and cyclic Hv1a (gray). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 4–5). There were no significant differences between native Hv1a and either analog (two-way ANOVA, p > 0.05, n = 3–5); (D,E) Effect of (D) 1,4-SeSe-Hv1a and (E) cyclic Hv1a (E) on the voltage-dependence of CaV channel activation. CaV channel currents were elicited by the pulse protocol shown above panel (E); Currents recorded in the presence of toxin were normalised to the maximum inward IBa in controls and fitted with Equation (1) (see Section 4.5). Data shows normalised IBa before (closed circles) and after (open circles and shaded) application of toxin. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 4–5).