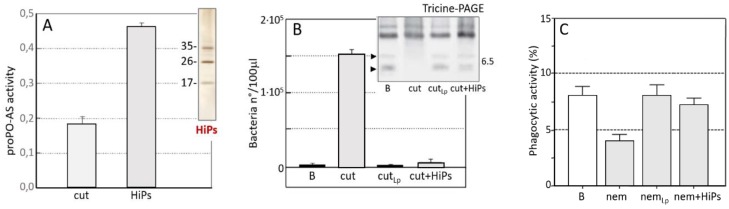
Figure 15.
Effects of S. feltiae and its cuticles on the host immune processes. (A): The activity of host proPO-AS, inhibited by the presence of S. feltiae cuticles, was restored by the addition of host-interacting proteins (HiPs) eluted from the parasite surface after co-incubation with host hemolymph. Inset: an SDS-PAGE of HiPs. (B): The presence of cuticles interferes with AMPs synthesis, since a marked growth of bacteria in the hemolymph from cuticle-injected larvae is observable (cut). Treatments with lipase (cutLp) or addition of HiPs (cut + HiPs), result in a marked bacterial clearance. Inset: presence/absence of AMPs bands after Tricine-PAGE analysis of hemolymph. (C): effects of S. feltiae on phagocytic activity of G. mellonella in the presence of: untreated nematodes (nem), lipase-treated nematodes (nemLp), nematodes plus purified HiPs (nem + HiPs). The presence of nematodes significantly reduces the phagocytosis, lipase treatments or HiPs addition, restore the phagocytosis activity, (from [99,146]).