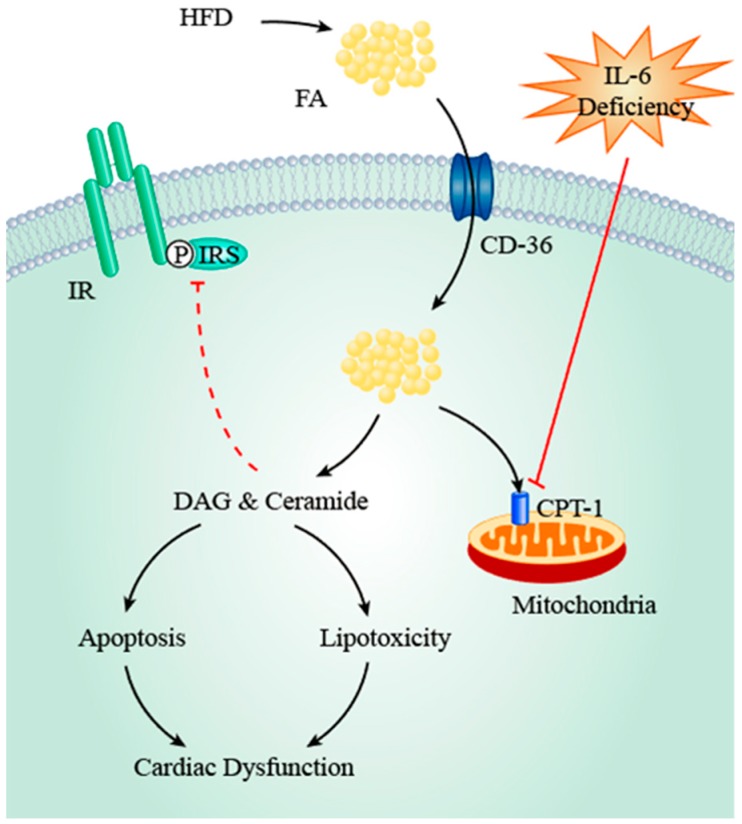
Figure 2.
The role of IL-6 deficiency in intramyocardial fatty acid accumulation. IL-6 deficiency upregulates CD36 which is the key protein carrier of fatty acid across plasma membrane, thereby enhancing myocardial fatty acid uptake and accumulation. Moreover, IL-6 deficiency inhibits CPT1 which is involved in fatty acid translocation into mitochondria, thereby exacerbating fatty acid excess. Due to the limited storage capacity, fatty acid deposits are converted into toxic lipid metabolites (e.g., DAG and ceramide) which result in cardiac insulin resistance and cellular apoptosis. Taken together, fatty acid per se and its metabolites lead to myocardial lipotoxicity. Black arrows: direct stimulatory effects or consequences of upstream factors; Red dashed arrows: multistep inhibitory effects; Red solid arrows: direct inhibition. FA, fatty acid; HFD, high-fat diet; DAG, diacylglycerol; CPT-1, Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I; IR, insulin receptor; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1.