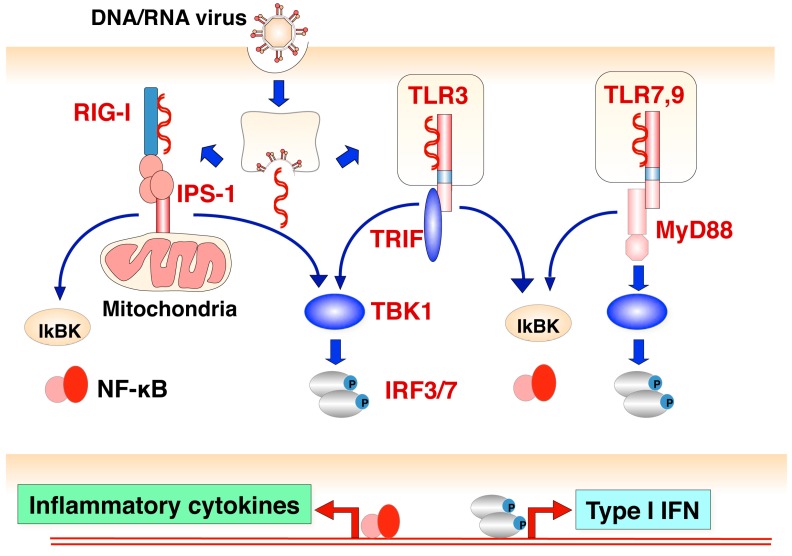
Figure 2.
Induction of innate immune response by viral infection. Induction of IFN and pro-inflammatory cytokines is mainly initiated by the recognition of several viral components in mammalian cells. RIG-like receptors such as RIG-I and MDA5 (cytoplasmic sensors) recognize viral-specific double strand RNA, and then the IPS-1-mediated signaling pathway is activated. On the other hand, Toll-like receptors such as TLR9, TLR7 and TLR3 (endosomal sensors) recognize viral DNA, RNA and replicative intermediate double strand RNA, and then a TRIF- or Myd88-mediated signaling pathway is activated. Finally, these pathways trigger the activation of transcription factors such as NF-κB and IRF3 or IRF7, followed by the production of inflammatory cytokines and Type I IFNs, respectively.