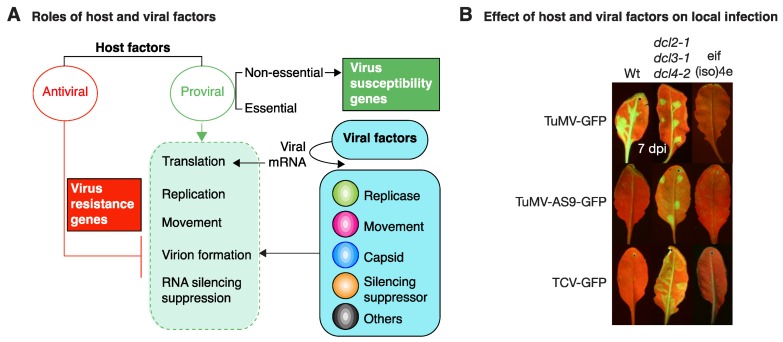
Figure 2.
Functional groups of host and viral factors based on their role in virus infection. (A) Host factors may have antiviral or proviral activity. Antiviral factors (red line) condition resistance to virus infection by antagonizing one or more essential parts of the infection cycle (dotted green box). Proviral factors (green arrow) work in synchrony with viral factors in all parts of the infection cycle, determine virus susceptibility, and may be essential or nonessential to the host. (B) Gene silencing restricts virus infection and virus-encoded silencing suppressors are needed for infection. In the absence of translation initiation factor eIS(iso)4E, TuMV cannot infect A. thaliana. eIF(iso)4E is needed for potyvirus replication and/or cell-to-cell movement. A. thaliana leaves were mechanically inoculated with TuMV-GFP, suppressor deficient TuMV-AS9-GFP, or suppressor deficient TCV-GFP. Pictures were taken at 7 dpi under UV light.