Table 2.
Cannabinoid receptors (CBRs) ligands and their effects shown in different animal models of MS (pertinent references are in parenthesis).
| Structure and Name | Origin and Activity | Animal Model and Effects |
|---|---|---|
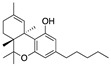
∆9-THC |
Phytocannabinoid CB1R partial agonist |
In EAE rats: amelioration of EAE progression [100]. In CREAE mice: amelioration of tremor and spasticity [102]. |
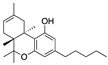
∆8-THC |
Phytocannabinoid CB1R ligand |
In EAE rats: amelioration of the clinical manifestations of EAE [101]. |
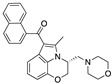
WIN-55212 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In CREAE mice: amelioration of tremor and spasticity [102]. In TMEV-infected mice: improvement of motor function on established neurological symptomatology; stimulation of the remyelination; reduction of microglial activation and of the number of CD4+ infiltrated T cells [105]. |
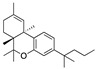
JWH-133 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In CREAE mice: amelioration of tremor and spasticity [102]. Intrathecal administration in EAE mice: reduction, dose-dependently, of both mechanical and cold hypersensitivity without any signs of ataxia or sedation [108]. |
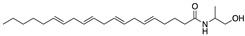
Methanadamide |
Endocannabinoid CB1R/CB2R agonist |
In CREAE mice: amelioration of tremor and spasticity [102]. |
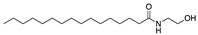
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) |
Endocannabinoid CB1R/CB2R agonist |
In CREAE mice: transient inhibition of spasticity [102]. |
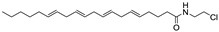
Arachidonyl-2-chloroethylamide (ACEA) |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB1R agonist |
In TMEV-infected mice: improvement of motor function on established neurological symptomatology; stimulation of the remyelination; reduction of microglial activation and of the number of CD4+ infiltrated T cells [105]. |
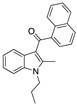
JWH-015 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In TMEV-infected mice: improvement of motor function on established neurological symptomatology; stimulation of the remyelination; reduction of microglial activation and of the number of CD4+ infiltrated T cells [105]. |
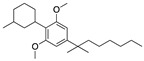
O-1966 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In the chronic EAE model: improved motor function; reduction of rolling and adhesion of endogenous leukocytes to pial microvasculature [106]. |
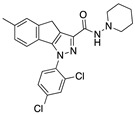
Gp-1a |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In EAE mice: reduction of clinical scores; amelioration of the recovery [107]. |
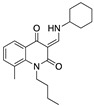
compound 21 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In EAE mice: reduction of the clinical scores and symptoms; decrease of leukocyte infiltration in the spinal cord and demyelination in white matter [109]. |
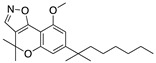
PM-226 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In TMEV-infected mice: dampening of neuroinflammation; reduction of microglial activation [110,111]. |
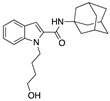
compound 57 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In EAE mice: alleviation of the clinical symptoms of EAE; protection of the murine central nervous system from immune damage; reduction of leukocyte infiltration and demyelination [112]. |
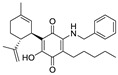
VCE-004.8 |
Synthetic cannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In EAE and TMEV mice: immunomodulatory activity; inhibition of inflammatory chemokines, chemokines receptors, and cytokines; inhibition of the expression of adhesion molecules (VCAM and ICAM-1); induction of the expression of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) [113]. |
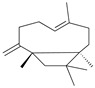
β-caryophyllene (BCP) |
Phytocannabinoid CB2R agonist |
In EAE mice: reduction of mechanical hyperalgesia, inflammation and pain [115]. |
