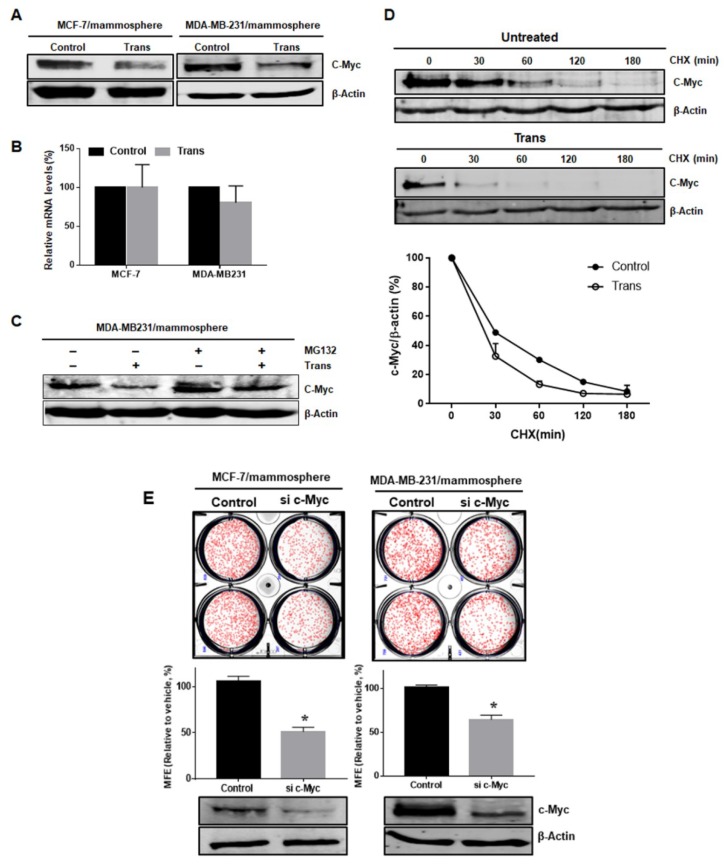
Figure 5.
The trans-coumaroyltormentic acid (Trans) promotes the proteasome-mediated degradation of c-Myc in breast CSCs. (A) Trans reduced the protein level of c-Myc. Cells were treated with Trans (20 μM) for 24 h. Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis with specific antibodies. β-Actin was used as an internal control. (B) Transcriptional expression of c-Myc genes of CSCs was determined in Trans- and DMSO-treated mammospheres using c-Myc-specific primers and real-time PCR. β-Actin served as an internal control. (C) Mammospheres were incubated with MG-132 and Trans (20 μM) for 24 h and lysed for Western blot analysis. (D) The cycloheximide (CHX) chase assays showing the half-life of c-Myc protein. The mammospheres were treated with CHX at 100 µg/mL for the indicated times. The half-life of endogenous c-Myc protein was measured by Western blot and analyzed. Each point represents the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. (E) Effect of c-Myc protein on mammosphere formation using siRNA knockdown of c-Myc. The mammospheres derived from siRNA-treated cells were cultured for seven days. Images were obtained by microscopy at 10× magnification and are representative mammospheres (scale bar = 100 μm). The data shown represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 vs. DMSO-treated control. All of the immunoblots are representative of more than three independent experiments.