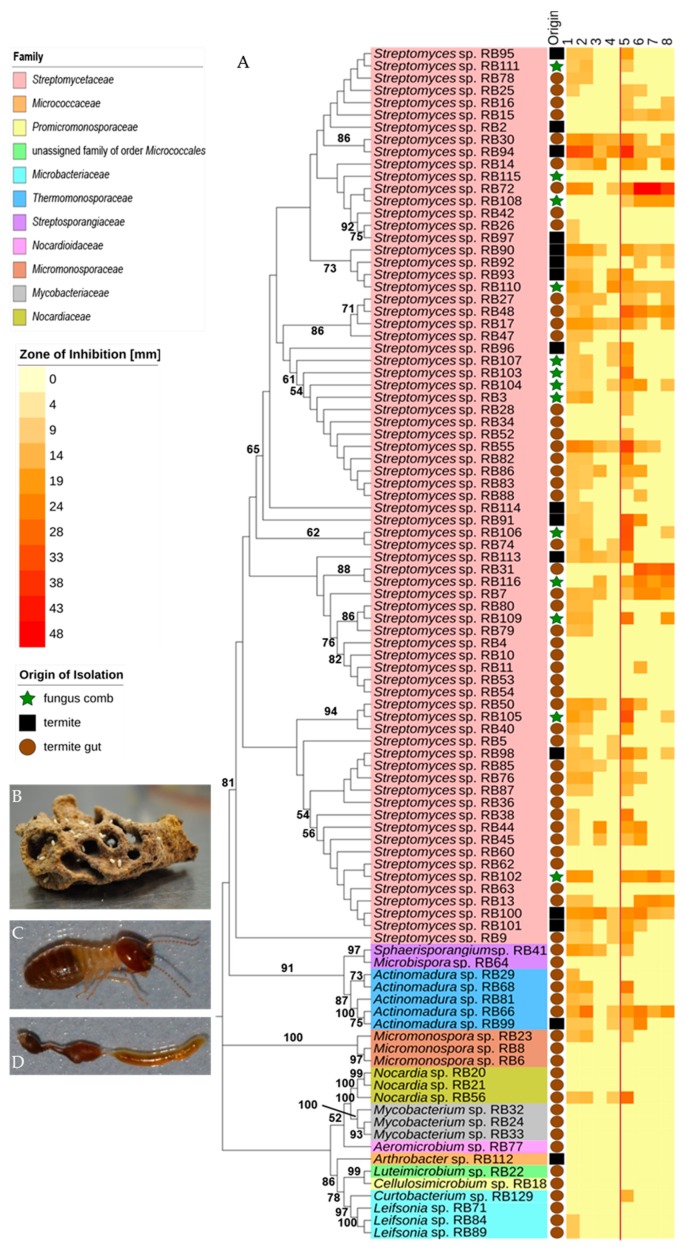
Figure 3.
Phylogeny and antimicrobial activity of newly isolated Actinobacteria: (A) Phylogenetic analysis based on near full-length 16S rRNA sequences of isolated Actinobacteria including phylogenetic placement to the family level. An unrooted neighbor-joining distance tree is shown with branch values indicating bootstrap support (>50 are given) of 1000 pseudoreplicates, tree was constructed with Mega 7.0 and edited with iTOL v3. Middle: Origin of isolation: termite abdomen: black box, termite gut: brown circle, fungus comb: green star. Right: activity heatmap against test strains Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 (1), Staphylococcus aureus IMET 10760 (2), Escherichia coli SG 458 (3), Pseudomonas aeruginosa K799/61 (4), Mycobacterium vaccae IMET 10670 (5), Sporobolomyces salmonicolor SBUG 549 (6), Candida albicans BMSY 212 (7) and Penicillium notatum JP36 (8). Representative picture of (B) fungus comb, (C) major worker, (D) dissected gut of major worker.