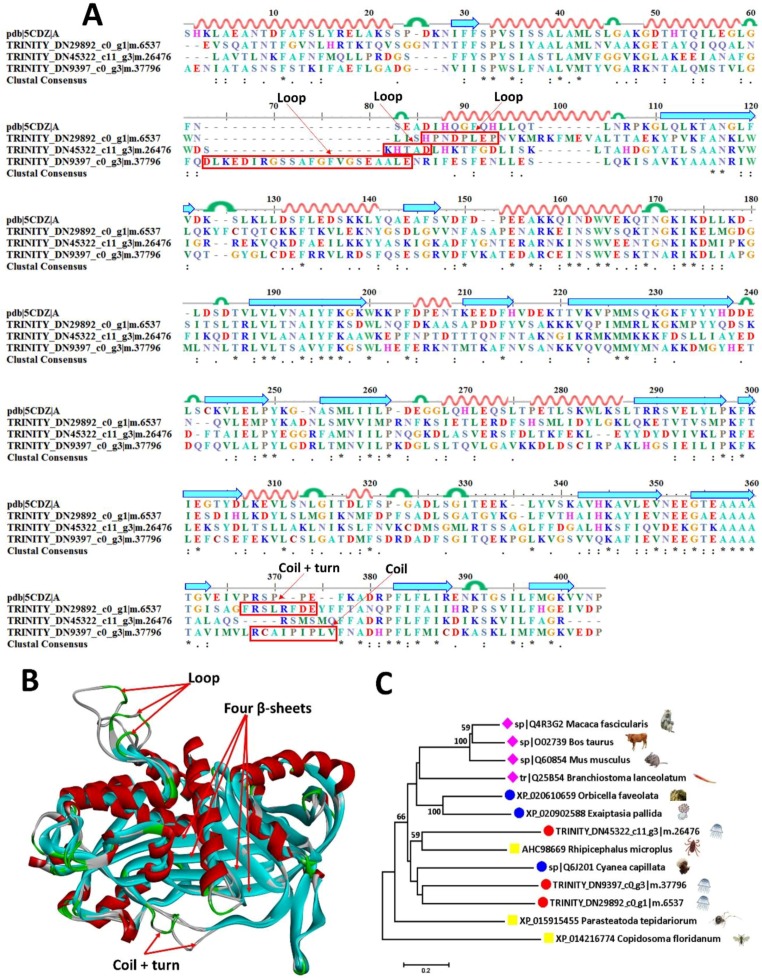
Figure 7.
Sequence alignment, 3D modeling and phylogenetic analysis of the putative serpins from A. coerulea. (A) Three putative sequences TRINITY_DN45322_c11_g3|m.26476, TRINITY_DN9397_c0_g3|m.37796, and TRINITY_DN29892_c0_g1|m.6537 in mucus-enriched proteins are aligned with a model serpin (pdb ID: 5CDZ). At the bottom of columns, asterisks (*) show conserved positions, colons (:) show conserved substitutions and points (.) show non-conserved substitutions. Grey line, green bend, blue banded arrowhead and red solenoid represent coil, turn, sheet and helix, respectively. Different fragments are framed by red lines. (B) 3D modeling was simulated using the template serpin (pdb ID: 5CDZ) by SWISS-MODEL and viewed by Discovery Studio 4.5. The colors grey, green, blue and red represent coils, turns, sheets and helices, respectively. Different fragments are indicated by red arrows. (C) Phylogenetic tree constructed by three putative serpins and 10 other sequences from different species using MEGA 7 with the Neighbor-Joining method.