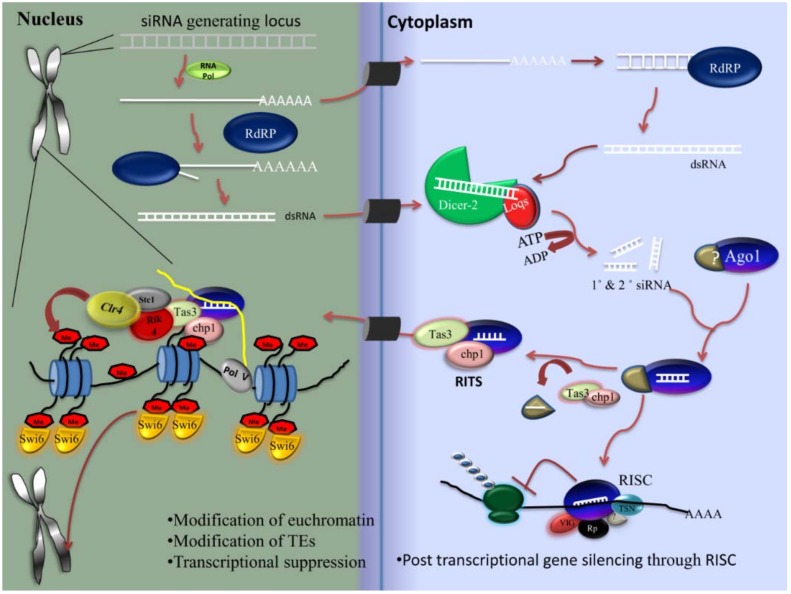
Figure 3.
Endogenous siRNA processing and role of these siRNAs in nucleus and cytoplasm. In the nucleus, siRNA-generating locus produces ssRNA, which is converted into dsRNA by RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in the nucleus and cytoplasm. In cytoplasm, this dsRNA is processed by Dcr2 and Loqs complex leading to the formation of endogenous duplex siRNA population (1° & 2° siRNAs duplex form), which is further converted into siRNA by the action of Ago1 and loaded to the RNA-induuced transcriptional silencing (RITS) complex. RITS is a multiprotein complex containing chromodomain protein chp1, argonaute interacting protein tas3. This complex is transported into the nucleus and binds with a nascent transcript in a sequence-specific manner, which leads to the recruitment of Stc1 and Rik4 proteins (the CLRC complex). This complex further recruits the Clr4, that is, methyltransferase, and attaches the methyl group on H3K9 (9th position of lysine in histone-3). H3K9 methylation stabilizes Swi6 (HP1 protein), which leads to the formation of heterochromatin or the silencing of transposons. In cytoplasm, the RISC complex is involved in post-transcriptional gene silencing.