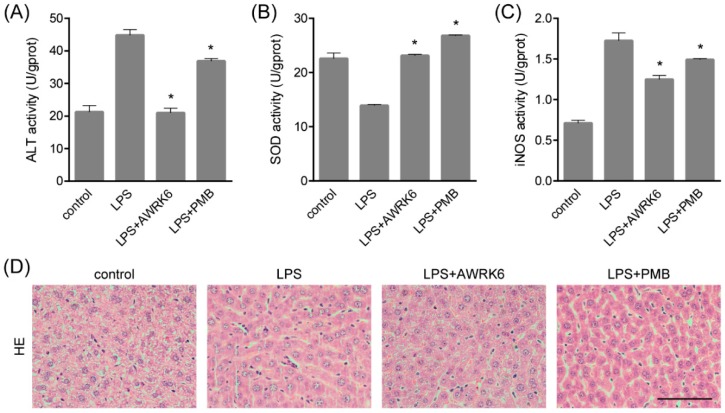
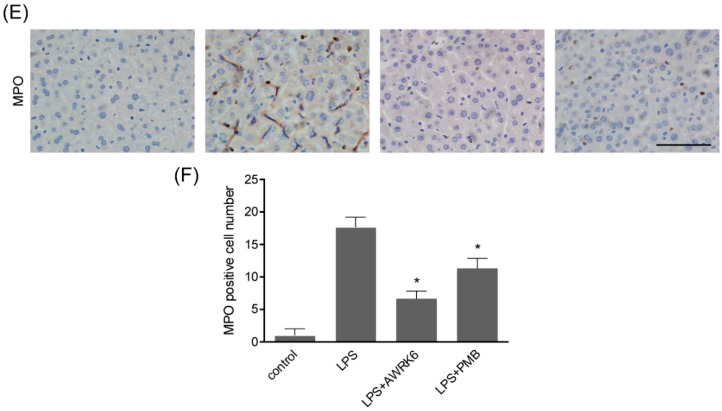
Figure 1.
AWRK6 relieved lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver injury in mice. The mice were administrated with LPS (50 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection. AWRK6 (10 mg/kg) or PMB (10 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally 1 h after LPS and an equal volume of sterile saline was used as a negative control. (A) The protective effect of AWRK6 on enhanced ALT activity in LPS-treated mice liver, assayed by Alanine aminotransferase Assay Kit. (B) The effect of AWRK6 on SOD activity in LPS-treated mice liver assayed by Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit. (C) The effect of AWRK6 on iNOS activity in LPS-treated mice liver, assayed by Nitric Oxide Synthase Assay Kit. (D) Histologic changes of liver tissues upon LPS and AWRK6 treatment, stained with HE. (E) Micrographs of liver sections stained with MPO antibody. (F) The analysis of liver sections stained with MPO was carried out using ImageJ. * p < 0.05 compared with the LPS groups. Scale bar indicates 100 μm.