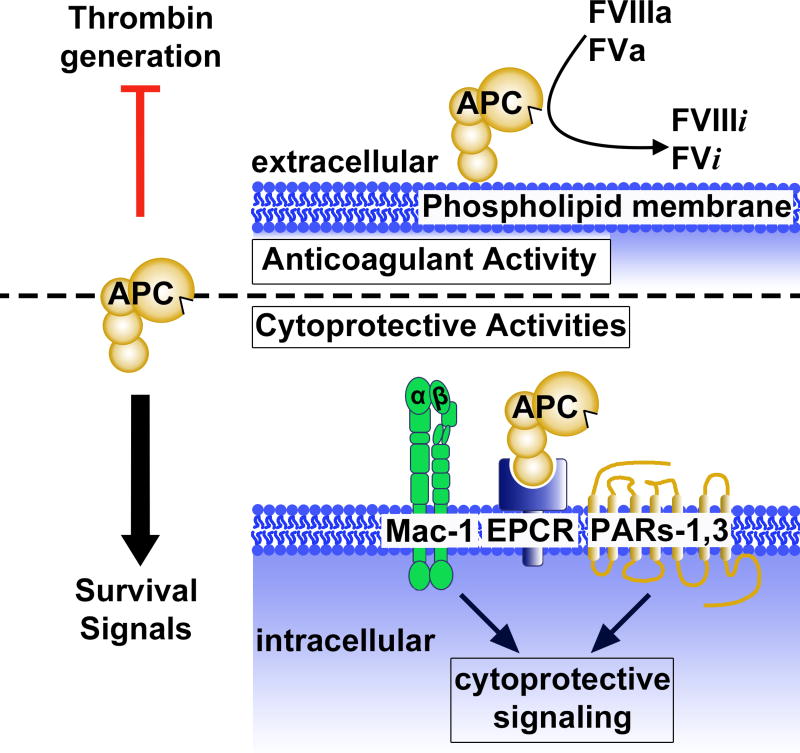
Figure 2. Anticoagulant and cytoprotective functions of activated protein C (APC).
APC has potent anticoagulant and cell survival effects. Thrombin generation is inhibited by APC on phospholipid membranes via proteolytic irreversible conversion of activated coagulation factors FVIIIa and FVa into their inactive forms, FVIIIi and FVi, respectively. APC also exerts diverse cytoprotective activities, including promotion of cell survival, by binding to select cell surface receptors, including Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) and endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), and by subsequent activation of protease activated receptors (PAR)1 and PAR3 to promote intracellular cytoprotective signaling. Figure adapted from [20].