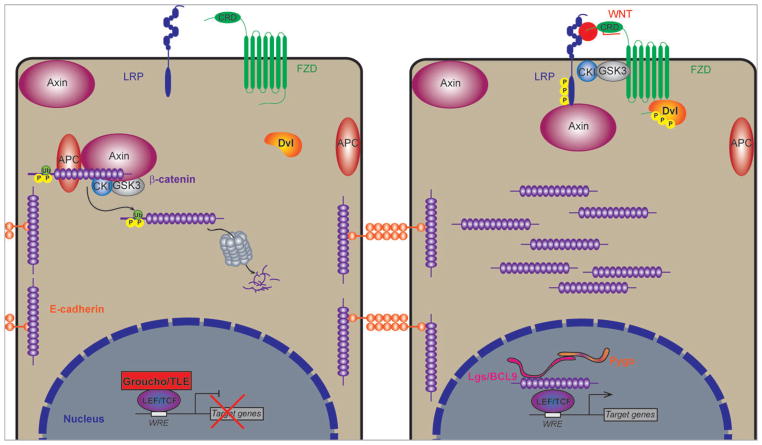
FIGURE 4.
β-catenin mediated Wnt signaling. In the absence of a Wnt ligand, β-catenin is sequestered by the multiprotein “destruction complex,” where it is phosphorylated and ubiquitinated, and targeted for proteasomal degradation. In the nucleus, LEF/TCF (lymphoid-enhancing factor/T-cell factor) transcription factors are resident on Wnt responsive elements (WREs), and recruit corepressors, such as Groucho/TLE. Upon Wnt-Fzd interaction, LRP oligomerizes with the receptor-ligand complex, and the destruction complex is dissociated. This leads to an accumulation of β-catenin in the cytosol, and eventual translocation to the nucleus, where it interacts directly with LEF/TCF transcription factors, and other transcriptional coactivators to initiate target gene expression