FIGURE 2.
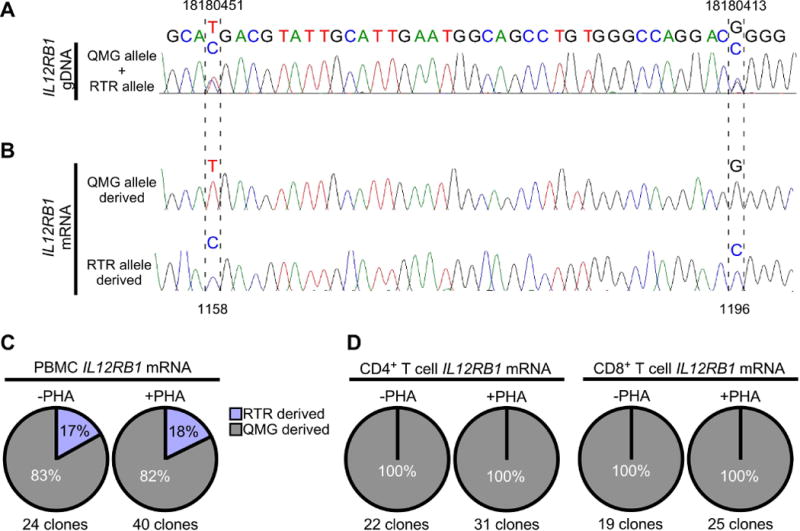
Allele-biased IL12RB1 expression in human PBMCs and T cells. PBMCs were isolated from 9 healthy adults; one PBMC portion was immediately lysed for gDNA/mRNA extraction, while the other portion was cultured with stimulant (PHA) prior to gDNA/mRNA extraction. PBMCs from 3 donors were further used to isolate CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, before (-PHA) and after PBMC stimulation (+PHA). PBMC gDNA was amplified with primers flanking 2 polymorphic sites in IL12RB1 exon 10 (18180451 and 18180413) that are constituents of the QMG allele (18180451T and 18180413G) or RTR allele (18180451C and 18180413C). Shown in (A) is the Sanger trace of a donor who was heterozygous for the QMG and RTR alleles, as indicated by 2 nts at gDNA positions 18180451 (T/C), and 18180413 (G/C). (B) mRNA from the same PBMC and T cell preparations (-PHA and +PHA) was used to generate donor- and cell-specific IL12RB1 cDNA libraries. From each library, multiple cDNA clones were randomly selected for Sanger sequencing. Shown are representative Sanger traces of clones transcribed from the QMG allele (top) and RTR allele (bottom); in contrast to the gDNA traces, there is only 1 nt present at each cDNA position, representing the gDNA allele from which that mRNA was originally transcribed. Indicated by hatched lines are the 2 cDNA positions (1158 and 1196) that correspond to nts transcribed from the gDNA SNPs above (18180451 and 18180413, respectively). (C-D) Pie charts depicting the relative representation QMG-derived cDNA clones (gray) and RTR-derived cDNA clones (blue) in (C) -PHA and +PHA PBMC preparations, and (D) -PHA and +PHA T cell preparations. Percentages are taken from the pooled Sanger sequencing data of all donors. The total number of clone sequences analyzed in this manner is indicated below each chart.
