FIGURE 5.
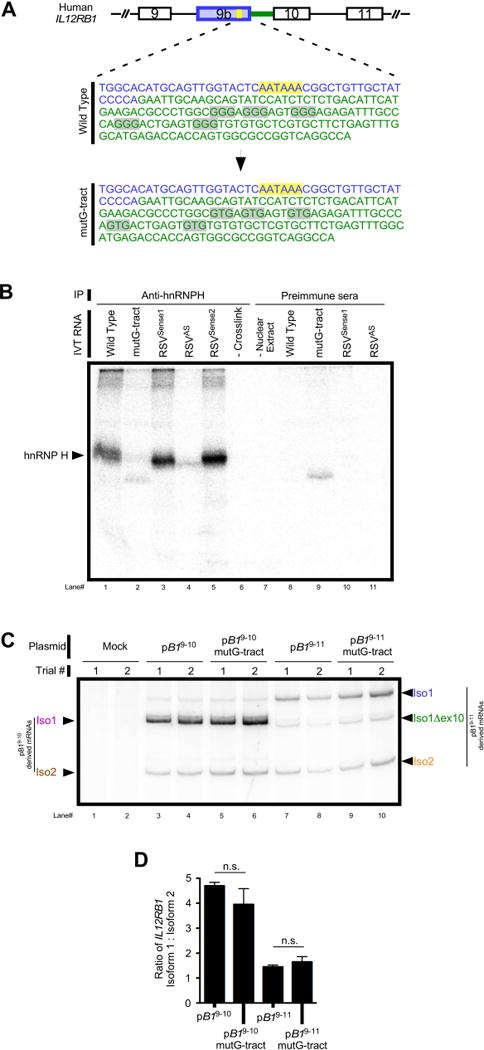
hnRNP H physically associates with IL12RB1 mRNA in a G-tract dependent manner. (A). Putative hnRNP H binding sites are located in the intron between exons 9b-10 (gray highlight) and comprises five GGG repeats (G-tracts). The exon 9b polyadenylation signal (yellow highlight) and 3' RNA terminus (blue) are shown for reference. Green denotes intron sequence. IL12RB1 minigenes were generated in which all five G-tracts were mutated from GGG (wild type) to GTG (mutG-tract). (B) To determine if hnRNP H physically associates with IL12RB1 pre-mRNAs at these sites, radiolabeled transcripts containing wild type (lane 1) or mutant (lane 2) IL12RB1 G tracts were incubated in HeLa nuclear extract, UV cross-linked, immunoprecipitated with anti-hnRNP H, and resolved using SDS-PAGE/autoradiography. RSVSense1 (lane 3) and RSVSense2 (lane 5) are positive control RNAs known to bind hnRNP H58; the antisense of RSVSense1 served a negative control (RSVAS, lane 4). Additional controls include wild type IL12RB1 RNA that was not crosslinked prior to immunoprecipitation (–Crosslink, lane 6), and a control reaction containing no HeLa nuclear extract (lane 7). Lanes 8-11 are control reactions immunoprecipitated using a nonspecific preimmune sera. (C) Jurkat cells were transfected with either pB19–10, pB19–10mutG-tract, pB19–11, or pB19–11mutG-tract (a derivative of pB19–11 harboring mutant G-tracts); minigene-derived Iso1 and Iso2 expression was assessed 2 days later by semi-quantitative PCR. Arrows on the left indicate which amplicons correspond to pB19–10-derived and pB19–10mutG-tract-derived Iso1 and Iso2 mRNA; arrows on the right indicate which amplicons correspond to pB19–11-derived and pB19–11mutG-tract-derived Iso1 and Iso2 mRNA. (D) Quantitation of the above semi-quantitative PCR.
