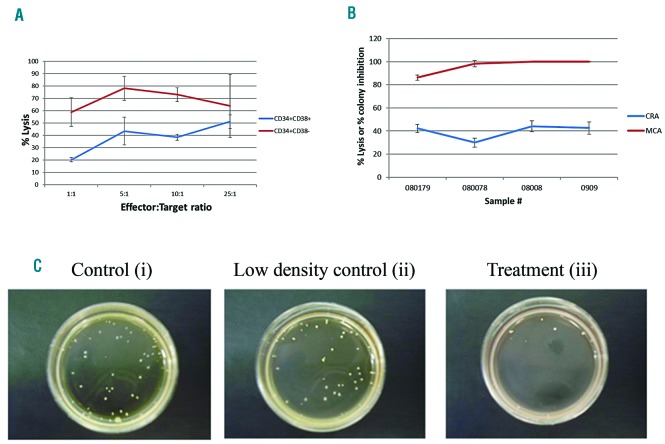
Figure 2.
NK-92 cytotoxicity against sorted leukemic stem cells and clonogenic leukemic cells relative to bulk leukemia cells. (A) Primary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) samples were sorted into CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ fractions for subsequent testing in a chromium release assay with NK-92 at a 25:1 E:T ratio. Data are presented as the mean percent (%) lysis of triplicate samples (+/−Standard Deviation) representative of two separate experiments. (B) Four primary AML samples were incubated with or without NK-92 at a 25:1 E:T ratio for 4 hours in 96-well U bottom plates and utilized in either a chromium release assay (CRA) or a methylcellulose cytotoxicity assay (MCA) conducted on the same day. The % lysis values and % colony inhibition values are plotted together (B). An example of the methylcellulose cytotoxicity assay (C) shows a representative assay for one sample (080179) with a control (AML only) (i), low density control (AML + NK-92 infused into methylcellulose only) (ii), and treatment group (AML + NK-92 co-incubated together in a 96-well plate well and then infused in methylcellulose) (iii).