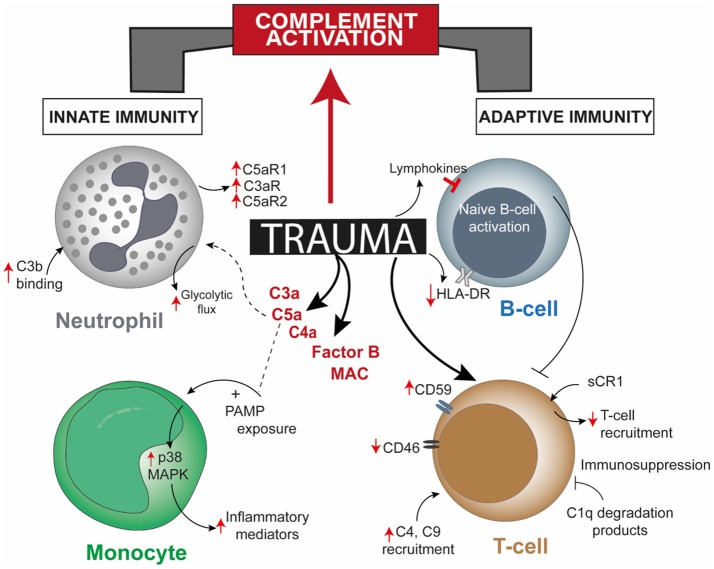
Figure 1.
Overview of post-trauma complement activation bridging altered cellular responses of the innate and the adaptive immune system. Trauma alters one or more cellular responses of neutrophils, monocytes, and B-cells and by directly modulating complement regulatory proteins on T-cells, apart from robust activation of complement factors. Though there is a direct effect of trauma on T-cells and B-cells, involvement of mediating complement factors are unreported. CR1, complement receptor 1; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen—antigen D Related; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern.