Figure 3.
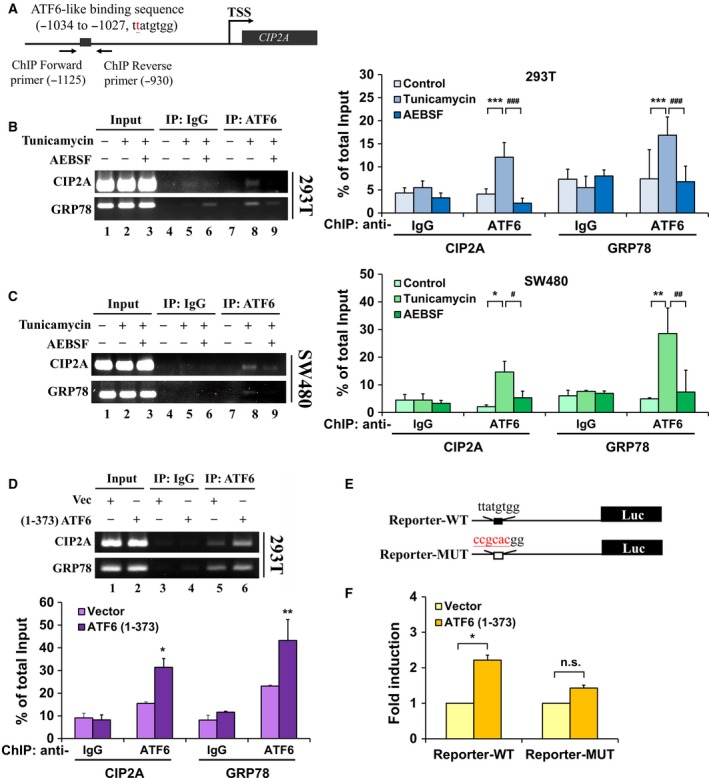
ATF6 directly regulates CIP2A gene transcription through binding to the CIP2A promoter. Scheme representing the region for ChIP primers flanking within the CIP2A promoter (A). HEK293T (B) and SW480 cells (C) were treated with tunicamycin (5 μg·mL−1) or AEBSF for 6 h; cells were harvested for ChIP assays using anti‐IgG and anti‐ATF6 antibodies, and precipitated DNA was used to amplify the PCR product of CIP2A and GRP78 promoters. After transfecting either pCGN‐vector or pATF6 (1–373) in HEK293T cells for 48 h, the DNA‐binding ability of ATF6 to the CIP2A and GRP78 promoters was analyzed using ChIP assays (D). The quantitative and statistical analysis was shown. Means of three independent experiments performed at least in triplicate are shown. Scheme representing the constructs of the CIP2A reporter (E). After transfection with either pCGN‐vector or pATF6 (1–373) for 48 h, cells were harvested, and CIP2A‐dependent reporter gene activity was measured by luciferase assay (F). The means ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate are shown. Statistical analysis was carried out using Student's t‐test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001.
