Figure 8. Model describing consequences of Filamin A pre‐mRNA editing on p190Rho GAP localization, PLC and ROCK signaling, smooth muscle contraction, hypertension, aortic, and cardiac remodeling.
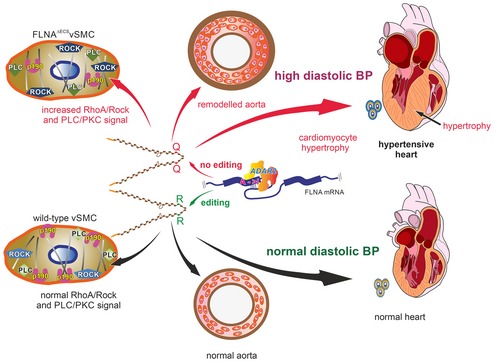
- (Top) Lack of editing in Filamin A pre‐mRNA produces a Filamin A isoform that only encodes a glutamine residue (Q) at position 2431. This leads to mislocalization of p190RhoGAP, misregulation of PLC and ROCK signaling, increased MLC phosphorylation, aortic hypercontraction, thickening of the smooth muscle layer, and increased perivascular collagen deposition. Loss of FLNA editing leads to persistently elevated diastolic blood pressure, left ventricular hypertrophy, and cardiac remodeling (Center). Filamin A pre‐mRNA editing by ADAR2 triggers a Q‐to‐R codon exchange at the end of exon 42 (Bottom). Edited FLNA helps localize p190RhoGAP to the cellular cortex where it can inhibit RhoA and regulate the activity of key smooth muscle contraction regulators such as PLC and ROCK machinery. This can maintain normal aortic function and normal diastolic blood pressure to preserve normal heart morphology.
