Figure 5. The interaction of EPCR1, ARID2, ARID3, ARID4, and TRB1 with the histone acetyltransferases HAM1 and HAM2 and the histone deacetylases HDA9 and HDA6.
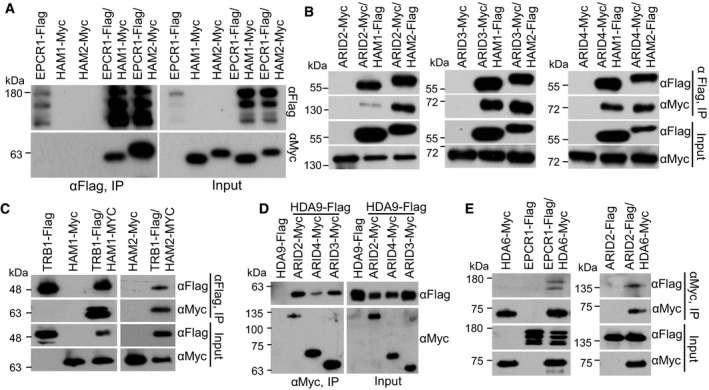
- The interaction of EPCR1 with HAM1 and HAM2. EPCR1‐Flag transgenic plants were crossed to HAM1‐Myc and HAM2‐Myc transgenic plants. The progeny were used to evaluate the interaction between EPCR1 with HAM1 and HAM2 by co‐IP.
- The interaction of ARID2, ARID3, and ARID4 with HAM1 and HAM2. ARID2‐Myc, ARID3‐Myc, and ARID4‐Myc transgenic plants were crossed to HAM1‐Flag and HAM2‐Flag transgenic plants, and their progeny were used for co‐IP.
- The interaction of TRB1 with HAM1 and HAM2. TRB1‐Flag transgenic plants were crossed to HAM1‐Myc and HAM2‐Myc transgenic plants, and their progeny were used for co‐IP.
- The interaction of HDA9 with ARID2, ARID3, and ARID4. ARID2‐Myc, ARID3‐Myc, and ARID4‐Myc transgenic plants were crossed to HDA9‐Flag transgenic plants, and their progeny were used for co‐IP.
- The interaction of HDA6 with EPCR1 and ARID2. EPCR1‐Flag and ARID2‐Flag transgenic plants were crossed to HDA6‐Myc transgenic plants, and their progeny were used for co‐IP.
Source data are available online for this figure.
