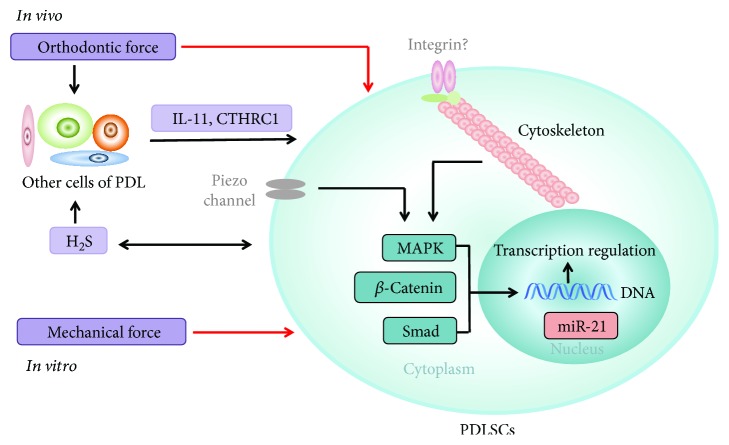
Figure 1.
The mechanical forces could act directly on PDLSCs both in vitro and in vivo (red arrows), while in vivo, they may influence PDLSCs indirectly through the factors secreted by other PDLCs (black arrows). A variety of molecules is involved in regulating the fate of PDLSCs after the application of force. IL-11, CTHRC1, miR-21, and H2S have been shown to help in transducing orthodontic force signals to PDLSCs. The cytoskeleton and MAPK, TGF-β/Smad, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways also play important roles in it.