FIGURE 1.
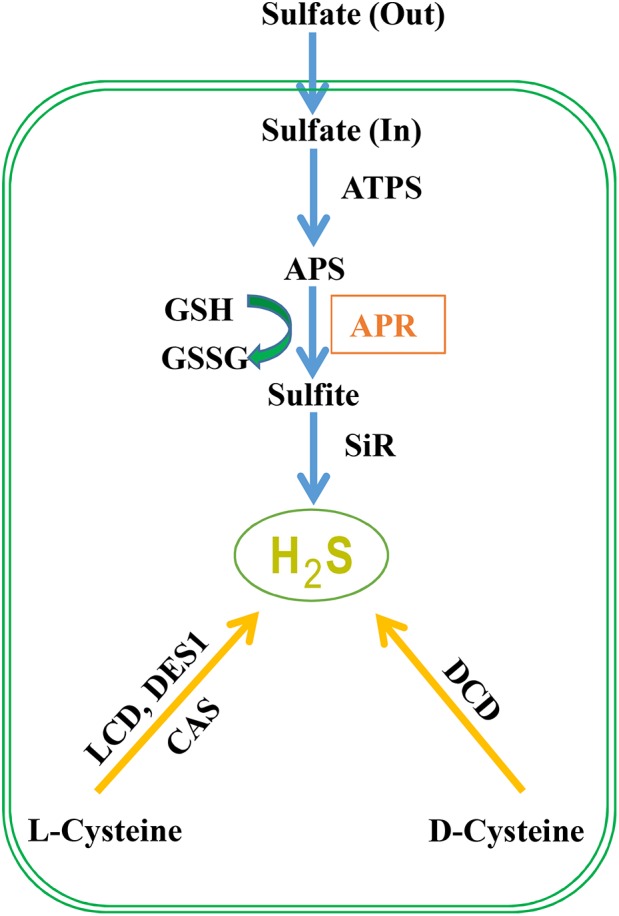
H2S metabolism in plants. Sulfate absorbed by plant roots through sulfate transporters is activated to APS (5′-adenylylsulfate) via ATP sulfurylase. APS can be reduced to sulfite by APR (APS reductase) which is further reduced to H2S by sulfite reductase. Subsequently, H2S is incorporated to cysteine (Cys), which is the first organic product of sulfur assimilation, and the starting point for methionine synthesis. Besides, cysteine is involved in the biosynthesis of coenzymes and vitamins including coenzyme A, biotin, thiamine, lipoic acid, and SAM (S-adenosyl-L-methionine) which is the donor of methylation. Besides the route of S-assimilation, H2S can also be produced from cysteine via the action of L-cysteine desulfhydrase (LCD), D-cysteine desulfhydrase (DCD), and DES1 which is member of O-acetylserine thiol lyase (OASTL) family proteins. Cyanoalanine synthase (CAS) generates cyanoalanine co-formed with H2S with cyanide and cysteine as the substrates.
