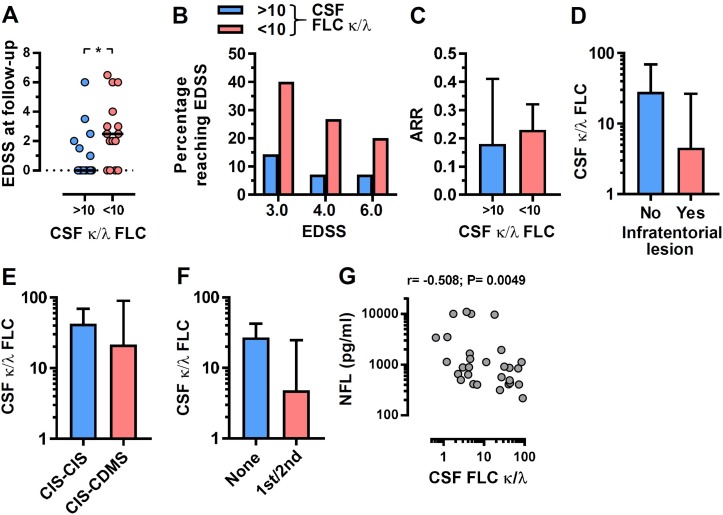
Figure 2.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) κ:λ free light chain (FLC) ratio predicts disability accumulation in multiple sclerosis (MS). (A) Expanded disability status scale (EDSS) at 5-year follow-up (following diagnostic lumbar puncture; where available) for high (>10) and low (<10) CSF FLC κ:λ ratio groups (n=15 and n=14, respectively); Mann-Whitney test; *p<0.05. The percentage of individuals reaching (B) EDSS 3.0, 4.0 or 6.0, (C) annualised relapse rates (ARR), (D) the presence of infratentorial lesions, (E) those remaining at clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) (CIS–CIS) or converting to clinically definite MS (CIS–CDMS) and (F) those requiring physician determined first-line or second-line therapy are shown for the high and low CSF κ:λ ratio groups. (G) Correlation between CSF neurofilament light chains and immunoglobulin FLC κ:λ ratios; Spearman correlation.