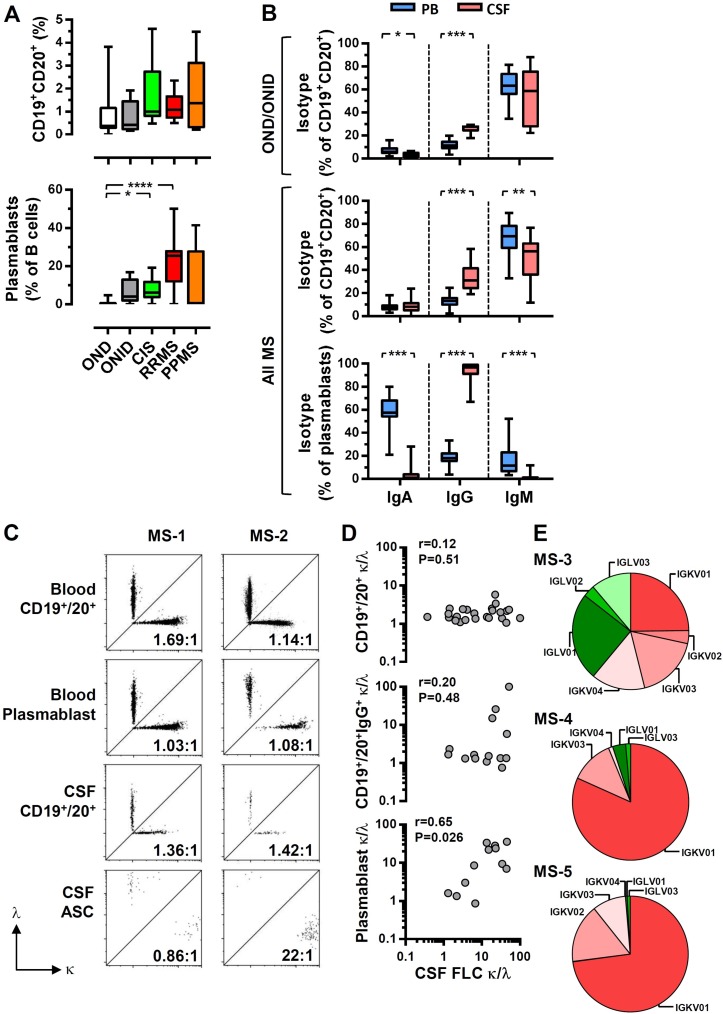
Figure 4.
The bias to κ light chain usage is intrinsic to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) plasmablasts. (A) The frequency of B cells (CD19+ and CD20+) and plasmablasts (according to the gating strategy in the online Supplementary figure e1) was determined for clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), primary-progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS), other neurological diseases (OND) and other neurological inflammatory diseases (ONID). (B) For CSF and matched peripheral blood samples, immunoglobulin (Ig)A, IgG and IgM isotypes were determined on both CD19+ CD20+ B cells and plasmablasts. Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s post-test; ***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05, all other comparisons non-significant (p>0.05). The frequency of κ-expressing and λ-expressing total B cells, IgG+ B cells and plasmablasts was determined by flow cytometry (C; representative plots for CIS (MS1) and RRMS (MS2)) and correlated with the CSF free light chain (FLC) κ:λ ratio (D); Spearman correlations. (E) The frequency of each Immunoglobulin Kappa Variable (IGKV); red and Immunoglobulin Lambda Variable (IGLV); green) gene segments was determined from the cDNA of CSF cells for MS3 (PPMS), MS4 (CIS) and MS5 (CIS).