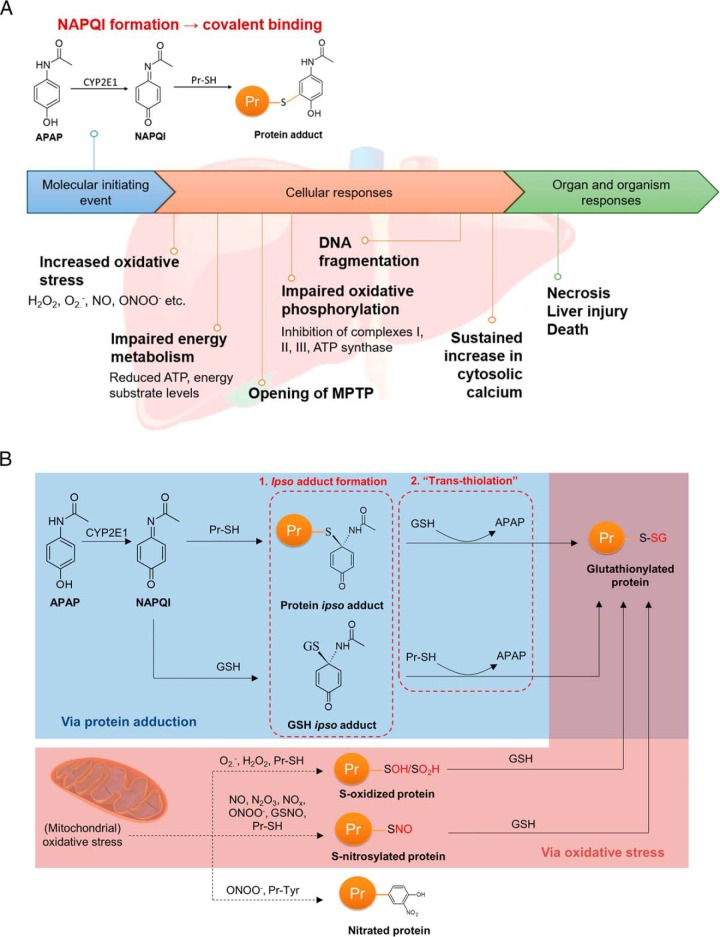
Fig. 1.
Profiling of APAP-induced glutathionylation. A, Key events in APAP-induced hepatotoxicity. The molecular initiating event begins with generation of NAPQI by CYP2E1, resulting in covalent adduction to protein thiols. The magnitude of covalent binding correlates with the degree of hepatotoxicity, and can be modulated by CYP450 inhibition or induction. Widespread covalent binding is thought to result in the key events listed under cellular responses, culminating in necrosis and liver injury. B, Mechanisms of APAP-induced glutathionylation: (1) via formation of a covalent ipso adduct between a protein or non-protein thiol with NAPQI, followed by glutathionylation, or (2) via thiol S-oxidation or S-nitrosylation by oxidative stress. It should be noted that the ipso adduct can also undergo an alternative rearrangement to the well-known thioether conjugates of APAP (9) which is not illustrated here for simplicity.