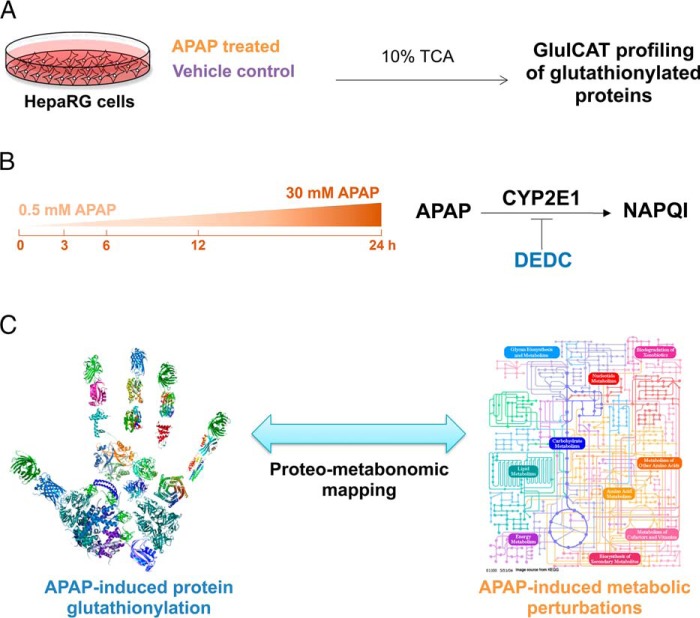
Fig. 2.
Overall experimental design for profiling APAP-induced glutathionylation. A, HepaRG cells were treated either with APAP or a vehicle control in biological triplicates, followed by harvesting of lysate in ice-cold 10% TCA and GluICAT profiling to identify glutathionylated proteins. B, APAP-induced glutathionylation was profiled longitudinally (3–24 h) using 30 mm APAP. The effect of dose (sub-toxic 0.5 mm versus 30 mm APAP at 3 h) was also examined. Finally the influence of APAP bioactivation by CYP2E1 on glutathionylation was investigated using the CYP2E1 inhibitor DEDC. C, Proteo-metabonomic mapping was applied to infer the functional consequences of protein glutathionylation and obtain insight into the perturbed pathways related to APAP toxicity.