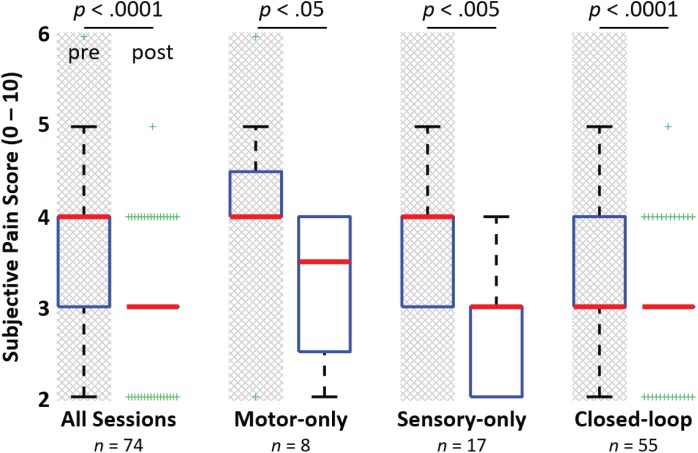
FIGURE 7.
Reduction in phantom limb pain after experimental sessions. The figure shows the median (bold red line), interquartile range (blue box), 1.5 times the interquartile range (black whiskers) and the outliers (green +’s). A significant reduction in phantom limb pain (Rank test; p < 0.0001) was observed between the subject’s pre-session and post-session subjective pain ratings for the 74 experimental sessions leading up to 14 months post-implant. A significant reduction in phantom pain was also observed for the subsets of sessions involving only motor control of a virtual or physical prosthesis, open-loop nerve microstimulation via USEAs in sensory-only sessions, and closed-loop sessions involving motor control and sensory feedback (Rank test; p < 0.05, p < 0.005, and p = 0.0001, respectively). Although full pain relief was not provided for any of these cases (e.g., overall, a median of 25% pain reduction was observed), the subject indicated that pain reduction is important and helpful for continuing with activities of daily living.