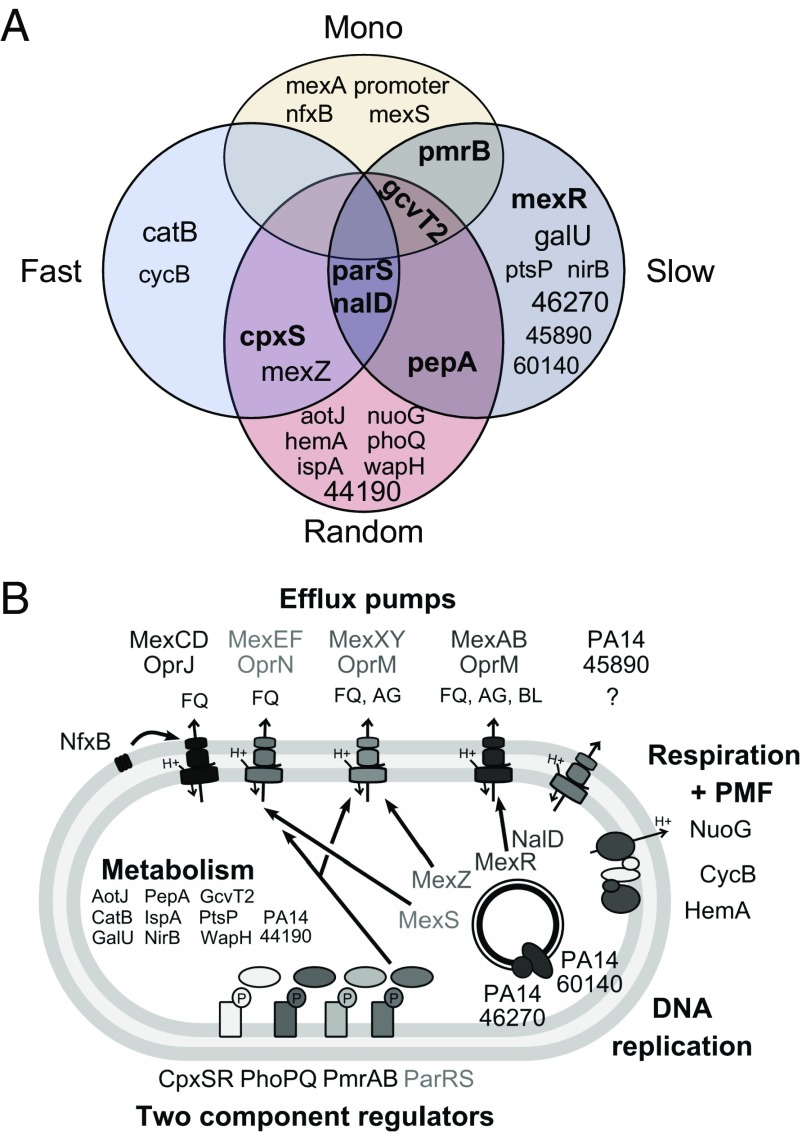
Fig. 4.
Genetic basis of adaptation. (A) Overlap of mutated genes among treatment types. Typeface and boldness indicate number of mutations in a gene. (B) Schematic of cellular functions targeted by adaptive evolution. Resistance is mostly achieved by mutations in two-component regulators or transcriptional regulators that control efflux pumps. AG, aminoglycosides; BL, β-lactams; FQ, fluoroquinolones; PMF, proton motive force.