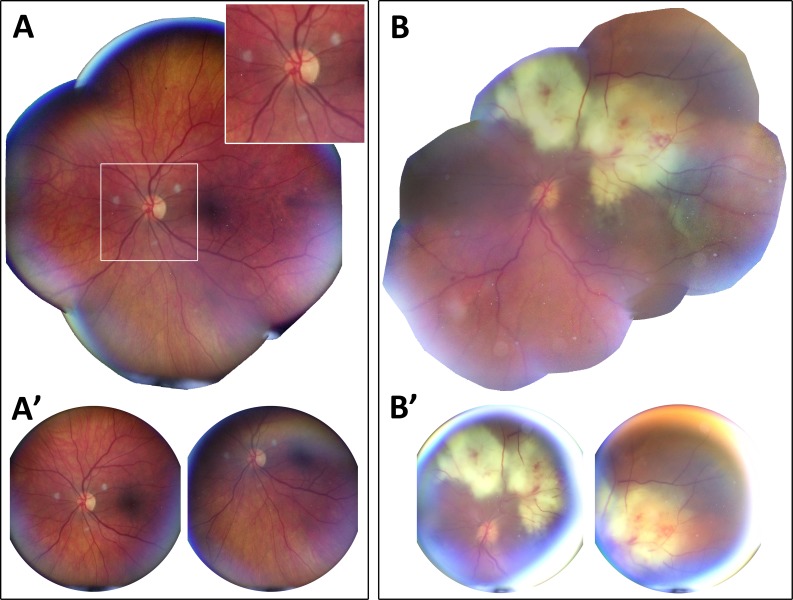
Figure 4.
Wide-field retinal imaging with CellScope Retina under typical and challenging imaging conditions in the inpatient setting. (A) Retinal montage of presumed fungal endophthalmitis in a patient with a well-dilated 8.0-mm pupil who was alert and cooperative with examination demonstrating three creamy white, well-circumscribed 500-μm lesions within 2 mm of the optic nerve. (A') Representative images used for retinal montage. Images A and A' were acquired in less than 1 minute by guiding the patient's eyes with device-assisted fixation. (B) Retinal montage of presumed fungal endophthalmitis in a hospitalized patient with a poorly dilated 4.5-mm pupil and altered mental status demonstrating a 16-mm large creamy white chorioretinal lesion with associated retinal hemorrhages, retinal vasculitis, and vitritis extending from the superior arcade into the macula and threatening the fovea. (B') Representative images demonstrating glare and restricted retinal view as present with small pupil size. These images were acquired in approximately 4 minutes by manually repositioning the angle of the device relative to the eye due to patient's inability to fixate. Multi-image processing steps are employed to improve wide-field viewing of the retina. All images were taken of bed-bound patients under normal inpatient care conditions without additional head stabilization or repositioning. (B, B′) Image stitching was performed using the i2k DualAlign software package.