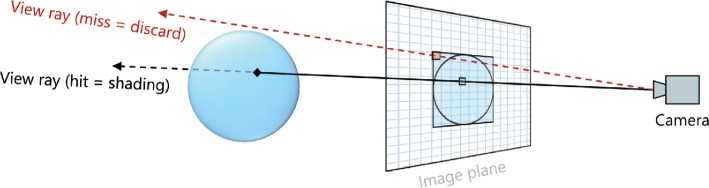
Figure 2:
Schematic drawing of GPU-based raycasting: for each sphere, a proxy geometry that covers the whole sphere is rendered (blue quad in the image plane). For each fragment of this quad, a view ray is computed in the pixel shader and a ray-sphere intersection determines whether the actual sphere is visible through this pixel. Our objective is to assess the rendering speed of the custom GPU used by HoloLens for such shader-based methods. We also compare this approach to traditional rendering methods based on triangle meshes.