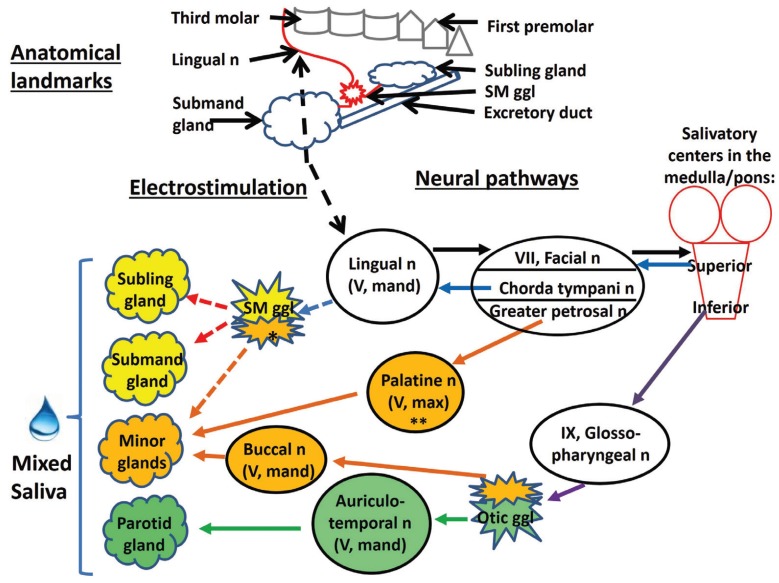
Figure 2.
The upper part (“Anatomical landmarks”) shows the location of the electrostimulation in relation to relevant anatomic structures: third molar, lingual nerve, submandibular ganglion and gland, sublingual gland and the excretory duct. It should be noted that the figure does not depict neither fibers that detach from the submandibular ganglion in direction to minor salivary glands nor the sensorial origins of the lingual nerve. The lower part (“Neural pathways”) provides an overview of the consequences of the lingual nerve electrostimulation (black dashed arrow) on the salivary reflex at the parasympathetic arm. The black full arrows represent afferent activity, while all other arrows denote efferent activity, as follows: - light blue arrows: fibers going up to the submandibular ganglion (SM ggl), - purple arrows: fibers going to the otic ganglion (Otic ggl), - red arrows: fibers originating from the submandibular ganglion and innervating the submandibular (Submand) and sublingual (Subling) glands, - orange arrows: fibers to the minor salivary glands (Minor glands), and - green arrows: fibers to the parotid gland. Dashed light blue, red and orange arrows denote fibers that carry impulses derived from both, direct and reflex stimulation. Other abbreviations: n (nerve), mand (mandibular branch), max (maxillary branch), ch (chorda), ggl (ganglion). The single asterisk indicates that the lingual nerve contributes to minor gland innervation also via Remak´s intralingual ganglia in addition to the submandibular ganglion, while the double asterisk denotes that the palatine nerve originates from the sphenopalatine ganglion (12). Note that sympathetic nerves can be expected to act on the glands as well, as an effect of the stimulation of the reflex arc. Reflexly elicited sympathetic impulses, originating from the upper thoracic paravertebral sympathetic trunk, reach their targets via sympathetic nerve fibers following the arteries of the glands; the relay between pre- and postganglionic sympathetic fibers is the superior cervical ganglion. However, the minor glands are thought to lack a sympathetic innervation of their acinar cells (12).