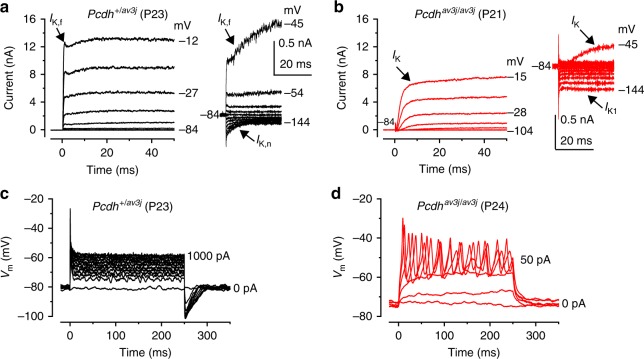
Fig. 1.
Current and voltage responses from IHCs of Pcdh15 mutant mice. a, b Potassium currents recorded from IHCs of control Pcdh15+/av3j (a) and littermate mutant Pcdh15av3j/av3j mice (b) using 10 mV depolarizing voltage steps from –84 mV to the various test potentials shown by some of the traces. The adult-type currents (IK,f and IK,n) were only present in IHCs from control Pcdh15+/av3j mice (a). IHCs from Pcdh15av3j/av3j mice retained the currents characteristic of immature cells (b, IK and IK1). The absence of the rapidly activating IK,f in Pcdh15 av3j/av3j IHCs is also evident when comparing the activation time course of the total outward currents on an expanded time scale (see insets). a, b are representative recordings from 10 (3 mice) and 12 (3 mice) IHCs, respectively. c, d Voltage responses elicited by applying depolarizing current injections to control, Pcdh15+/av3j c and mutant, Pcdh15av3j/av3j d IHCs from their resting membrane potentials. Depolarizing current injections caused slow APs in the Pcdh15avj3/av3j mutant IHC. c, d are representative recordings from 8 (3 mice) and 15 (3 mice) IHCs, respectively. Recordings were performed near body temperature