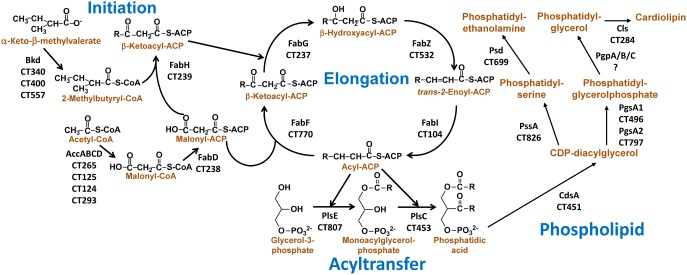
FIGURE 2.
Detailed diagram for fatty acid and phospholipid synthesis in C. trachomatis. From Yao et al. (Yao et al., 2015a). This figure shows the protein name designations along with the C. trachomatis gene locus number for each reaction. The biosynthetic pathway is divided into four modules. The initiation module consists of the enzymes that supply the precursors to initiate FASII. The elongation module sequentially elongates the acyl chain. The acyltransfer module extracts acyl-ACP from the elongation cycle to acylate glycerol-phosphate. The phospholipid module diversifies the headgroups to produce PE, PG, and CL. Despite a few minor quirks such as the plastidial related enoyl-ACP reductase (FabI) and 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (PlsE), fatty acid and phospholipid synthesis in C. trachomatis is the same as other free-living bacteria such as E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus.