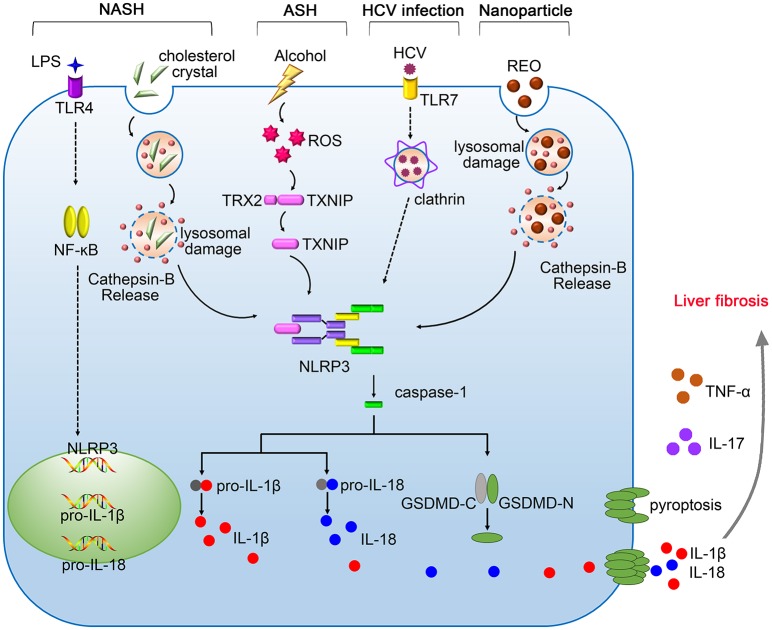
Figure 1.
The pathogenic roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in liver diseases. Gut-derived PAMPs, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), activate nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, promoting the expression of pro-IL-1β, and pro-IL-18. The NLRP3 inflammasome in the liver is activated by serious danger signals, such as cholesterol crystals, ethanol, and REO nanoparticles. Excessive alcohol consumption stimulates the generation of ROS, which facilitates the cleavage of TXNIP and contributes to assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome. The activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in response to HCV infection requires the recognition by Toll-like receptor-7 (TLR-7) and clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Pyroptosis features GSDMD pores on the membrane, allowing the release of IL-1β and IL-18 into the extracellular space. NLRP3 inflammasome cooperates with TNF-α and IL-17 contributing to the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis.