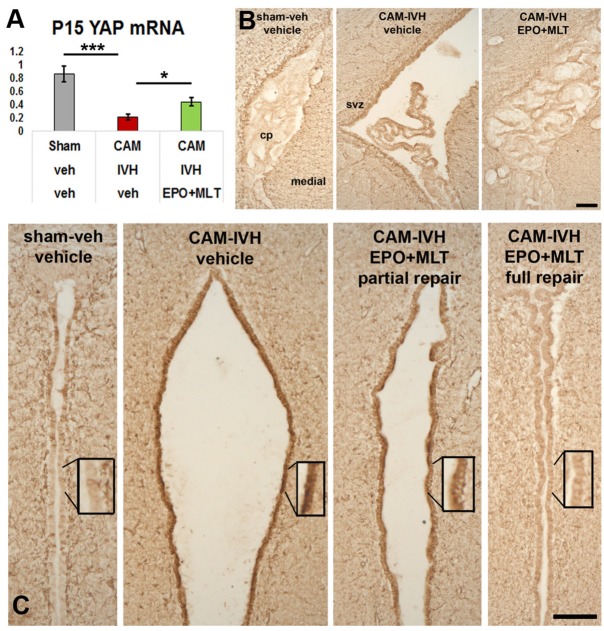
FIGURE 7.
Neonatal EPO+MLT treatment in CAM-IVH rats improves periventricular yes-associated protein (YAP) mRNA levels and reduces GFAP-expression. (A) At P15, periventricular YAP mRNA levels are reduced in micro-dissected ependyma from vehicle-treated CAM-IVH rats, compared to shams. This loss is partially, but significantly, prevented in CAM-IVH rats following EPO+MLT treatment. (B) GFAP-immunolabeling of coronal sections of the lateral ventricle show the choroid plexus appears shrunken in the large ventricle. EPO-MLT-treatment prevents this appearance of the choroid plexus. (C) Minimal GFAP-immunolabeling is present in the normal caliber third ventricle of a sham rat, while marked GFAP expression is present in the ependymal lining of the dilated third ventricle in a vehicle-treated CAM-IVH rat. In an EPO+MLT-treated CAM-IVH rat with mild ventriculomegaly, there is less GFAP present, and this pattern is more apparent in the EPO+MLT-treated CAM-IVH rat with a normal sized third ventricle (Bars = 100 microns, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).