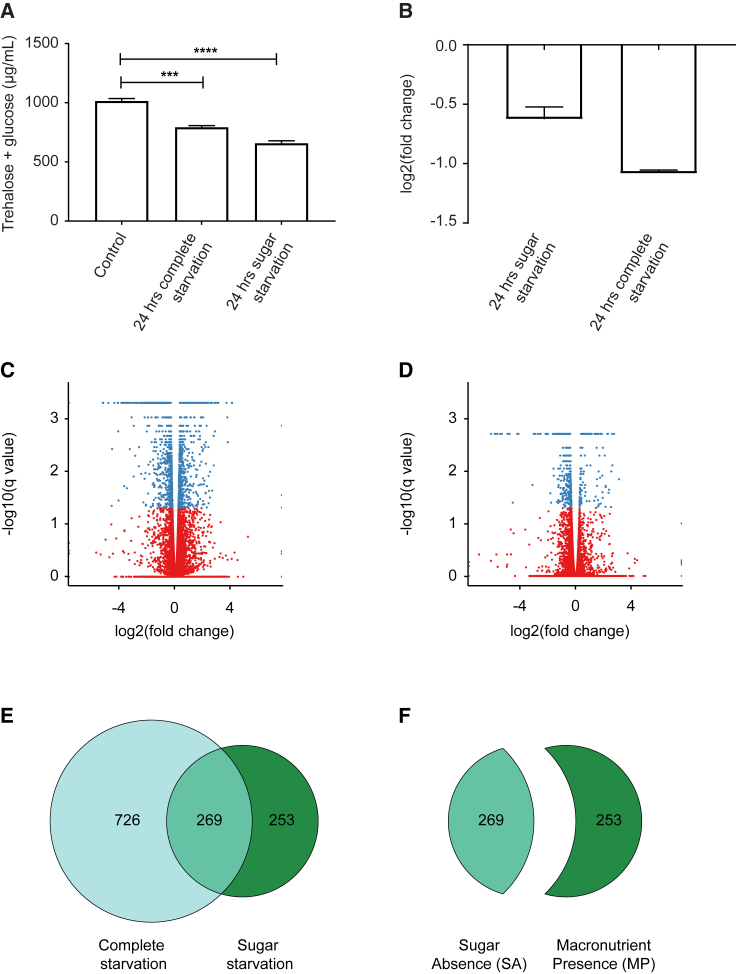
Figure 1.
Transcriptional Response of the Fly Brain to Sugar Starvation Is Distinct from the Response to Complete Starvation
(A) Combined levels of circulating trehalose and glucose are significantly decreased after 24 hr of sugar or complete starvation (n = 4). Error bars represent SEM. ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001.
(B) Transcript levels of ilp2 and ilp5 in the fly brain after 24 hr of sugar and complete starvation as measured by qRT-PCR (n = 4). Error bars represent SD.
(C and D) Volcano plots showing differentially expressed genes under conditions of complete starvation (C) and sugar starvation (D), comparing fold change values to their statistical significance levels. Blue dots represent differentially expressed genes with a q value ≤0.05 (significant change), while the red dots indicate those with q values >0.05.
(E) Venn diagram showing overlap of the differentially expressed genes after complete and sugar starvation.
(F) Two subsets of the sugar starvation dataset divided based on their overlap with the complete starvation dataset.
See also Figure S1.