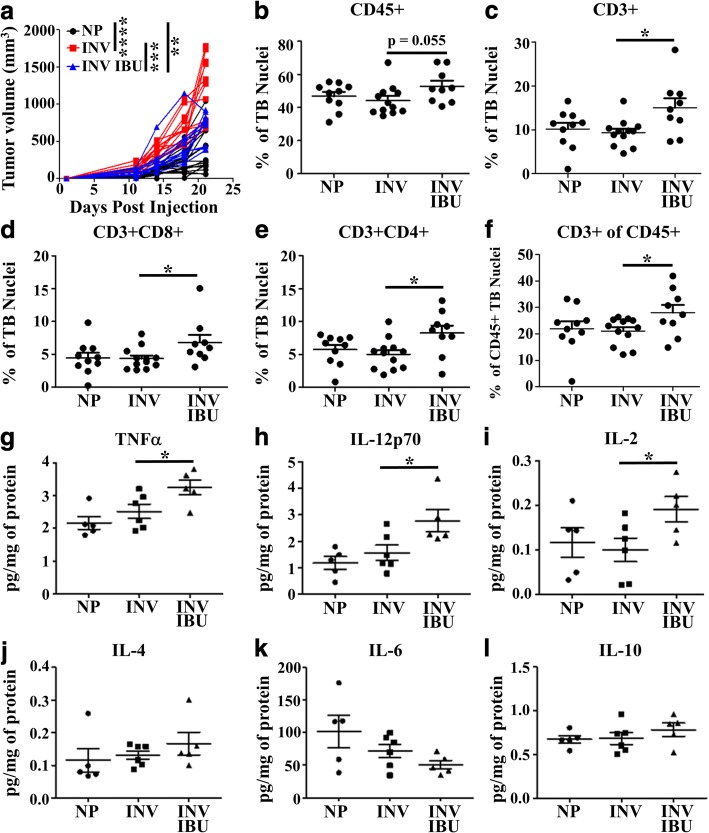
Fig. 5.
Ibuprofen enhances tumor border T cell abundance and intratumoral Th1/M1 related cytokines. A subset of study tumors a representative of tumor growth from their respective groups; involution (INV), involution with 300 mg/kg ibuprofen (INV IBU) and nulliparous (NP), were stained for immune cell populations using multiplex IHC and data analyzed by image cytometry. Abundance of b CD45+, c CD3+, d CD3 + CD8+, and e CD3 + CD4 + (CD8-) as percent of total nuclei at the tumor border (TB), and composition of f CD3 + CD4 + (CD8-) relative to the CD45+, demonstrate ibuprofen effects on T cell populations at the tumor border. g-l Frozen tumor samples were subjected to cytokine level detection to determine intratumoral protein levels of g TNFa, h IL-12p70, i IL-2, j IL-4, k IL-6, and l IL-10. Determination of statistically significant differences were based upon two-tailed Student’s t-test between the indicated groups with p < 0.05 (*)